|
I am an expert research scientist at United Imaging Intelligence (UII), Burlington MA. I obtained my PhD degree from ECSE Department of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. My advisor is Prof. Rich Radke. I received my master and bachelor degree from Beijing Institue of Technology, Beijing, China. Email / CV / Google Scholar / LinkedIn |

|
|
My research focuses on the design and development of interpretable deep learning systems and algorithms for a variety of computer vision and medical imaging applications, with particular focus on automated patient positioning and modeling, video analytics, image retrieval/person re-identification and generative modeling. Representative papers are listed as follows. |
|
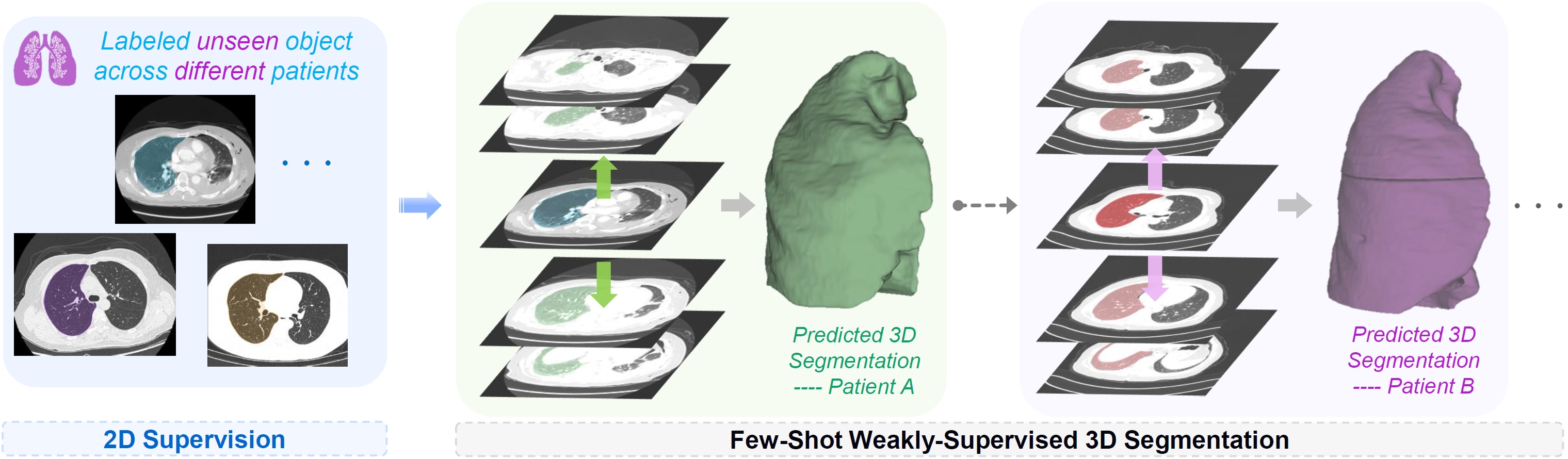
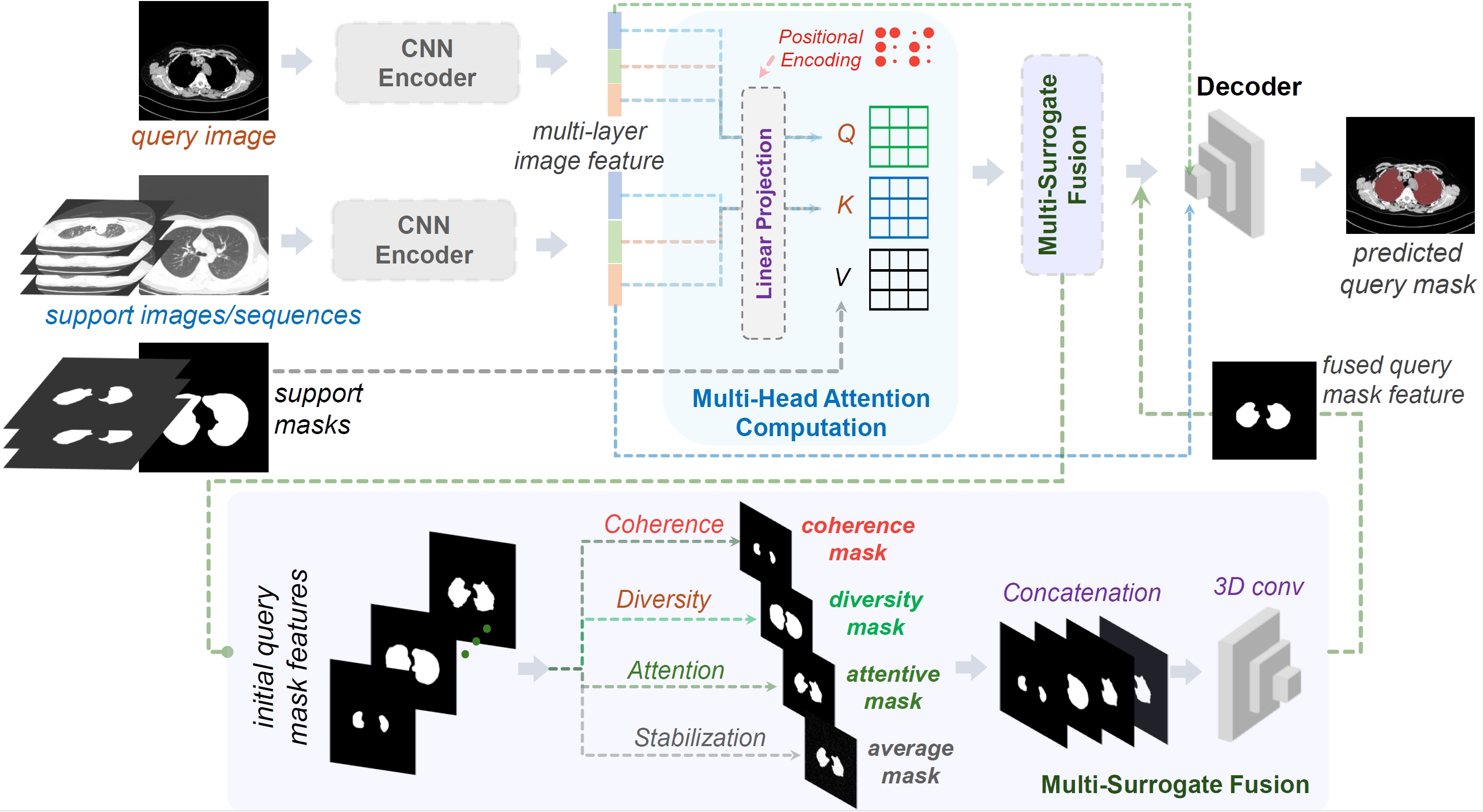
Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Zhongpai Gao, Terrence Chen, Richard J. Radke, Ziyan Wu MICCAI (early accept), 2024 We present MSFSeg, a novel few-shot 3D segmentation framework with a lightweight multi-surrogate fusion (MSF). MSFSeg is able to automatically segment unseen 3D objects/organs (during training) provided with one or a few annotated 2D slices or 3D sequence segments, via learning dense query-support organ/lesion anatomy correlations across patient populations. Our proposed MSF module mines comprehensive and diversified morphology correlations between unlabeled and the few labeled slices/sequences through multiple designated surrogates, making it able to generate accurate cross-domain 3D segmentation masks given annotated slices or sequences. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework by showing superior performance on conventional few-shot segmentation benchmarks compared to prior art, and remarkable cross-domain cross-volume segmentation performance on proprietary 3D segmentation datasets for challenging entities, i.e., tubular structures, with only limited 2D or 3D labels. |


|
Zhongpai Gao, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Xiao Chen, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu NeurIPS, 2024 We propose a novel approach that balances realistic physics-inspired X-ray simulation with efficient, differentiable DRR generation using 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Our direction-disentangled 3DGS (DDGS) method decomposes the radiosity contribution into isotropic and direction-dependent components, able to approximate complex anisotropic interactions without complex runtime simulations. Additionally, we adapt the 3DGS initialization to account for tomography data properties, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. |

|
Bin Wang, Anwesa Choudhuri, Meng Zheng, Zhongpai Gao, Benjamin Planche, Andong Deng, Qin Liu, Terrence Chen, Ulas Bagci, Ziyan Wu ICLR, 2024 We propose OIS: order-aware interactive segmentation, where we explicitly encode the relative depth between objects into order maps. We introduce a novel order-aware attention, where the order maps seamlessly guide the user interactions (in the form of clicks) to attend to the image features. We further present an object-aware attention module to incorporate a strong object-level understanding to better differentiate objects with similar order. Our approach allows both dense and sparse integration of user clicks, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency as compared to prior works. |

|
Zhongpai Gao, Benjamin Planche Meng Zheng, Anwesa Choudhuri, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu ICLR, 2024 We revisit 6D Gaussians and introduce 6D Gaussian Splatting (6DGS), which enhances color and opacity representations and leverages the additional directional information in the 6D space for optimized Gaussian control. Our approach is fully compatible with the 3DGS framework and significantly improves real-time radiance field rendering by better modeling view-dependent effects and fine details. The project page is: https://gaozhongpai.github.io/6dgs/ |

|
Qucheng Peng, Benjamin Planche, Zhongpai Gao, Meng Zheng, Anwesa Choudhuri, Terrence Chen, Chen Chen, Ziyan Wu ICLR, 2024 We propose a solution that adequately handles the distinct visual and semantic modalities, i.e., a 3D vision-language Gaussian splatting model for scene understanding, to put emphasis on the representation learning of language modality. We propose a novel cross-modal rasterizer, using modality fusion along with a smoothed semantic indicator for enhancing semantic rasterization. We also employ a camera-view blending technique to improve semantic consistency between existing and synthesized views, thereby effectively mitigating over-fitting. |

|
Wenqi Ren, Ruihao Xia, Meng Zheng, Ziyan Wu, Yang Tang, Nicu Sebe ACM MM, 2024 We propose a label alignment method by leveraging VLMs to relabel pseudo labels for novel classes. Considering that VLMs typically provide only image-level predictions, we embed a two-stage method to enable fine-grained semantic segmentation and design a threshold based on the uncertainty of pseudo labels to exclude noisy VLM predictions. To further augment the supervision of novel classes, we devise memory banks with an adaptive update scheme to effectively manage accurate VLM predictions, which are then resampled to increase the sampling probability of novel classes. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of our proposed method across various CCDA scenarios. |
|
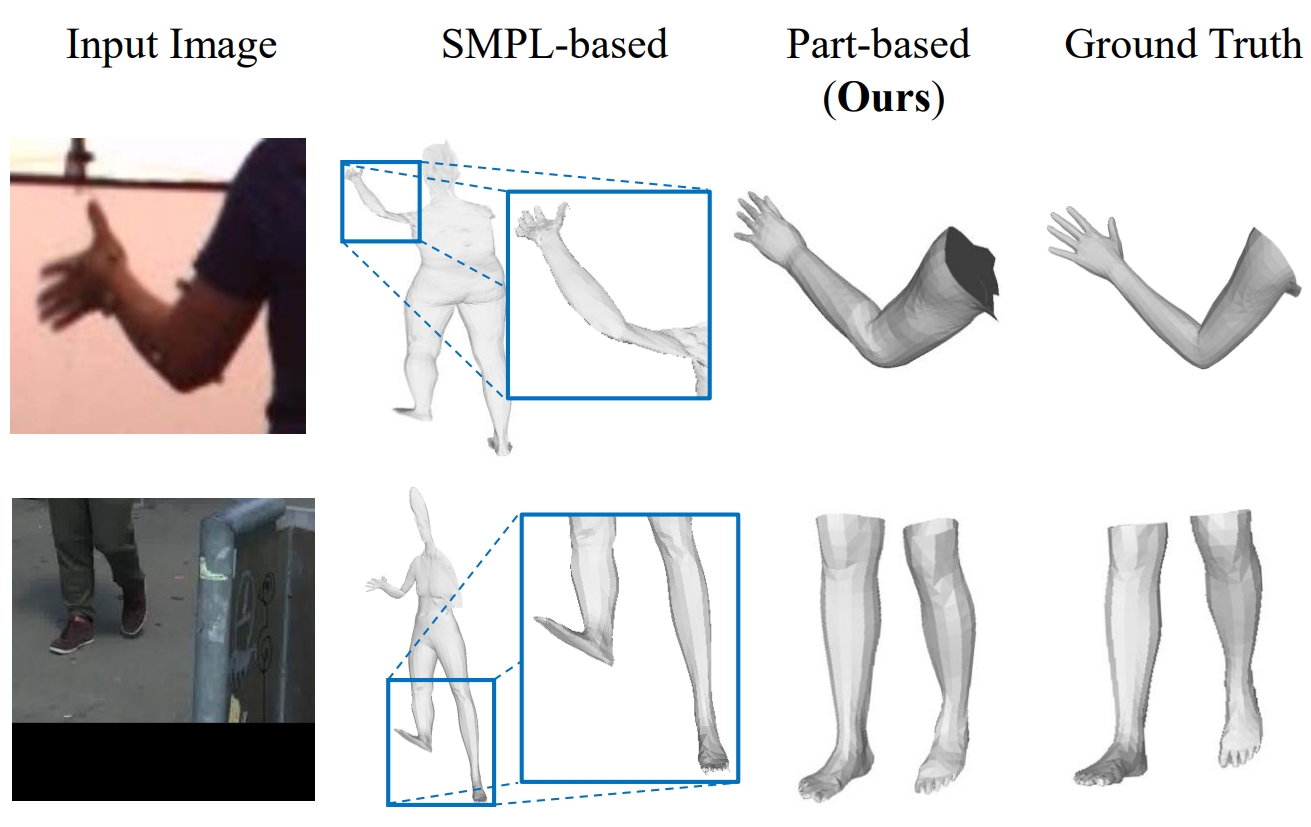
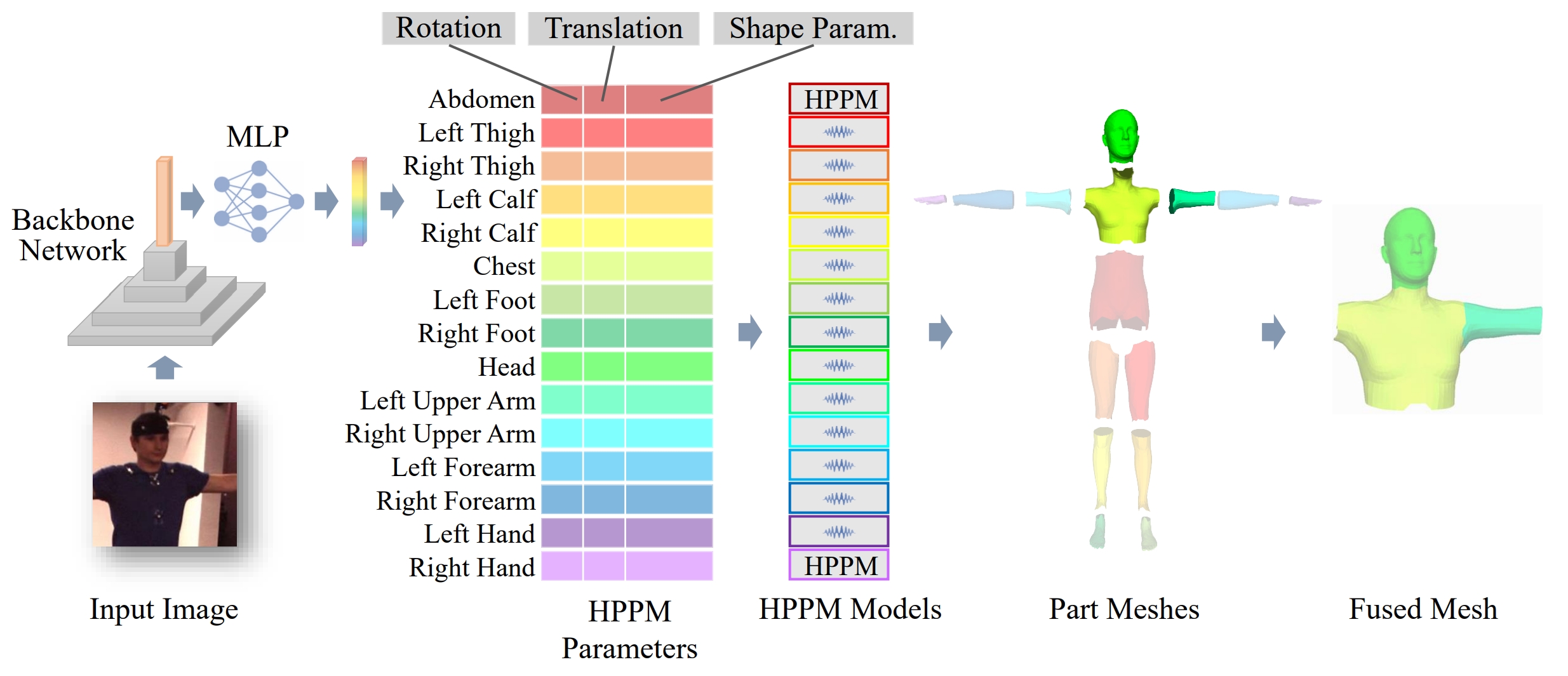
Tianyu Luan, Zhongpai Gao, Luyuan Xie, Abhishek Sharma, Hao Ding, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Ange Lou, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu ECCV, 2024 We introduce a novel bottom-up approach for human body mesh reconstruction, specifically designed to address the challenges posed by partial visibility and occlusion in input images. Traditional top-down methods, relying on whole-body parametric models like SMPL, falter when only a small part of the human is visible, as they require visibility of most of the human body for accurate mesh reconstruction. To overcome this limitation, our method employs a "Divide and Fuse (D&F)" strategy, reconstructing human body parts independently before fusing them, thereby ensuring robustness against occlusions. We design Human Part Parametric Models (HPPM) that independently reconstruct the mesh from a few shape and global location parameters, without inter-part dependency. A specially designed fusion module then seamlessly integrates the reconstructed parts, even when only a few parts are visible. |
|
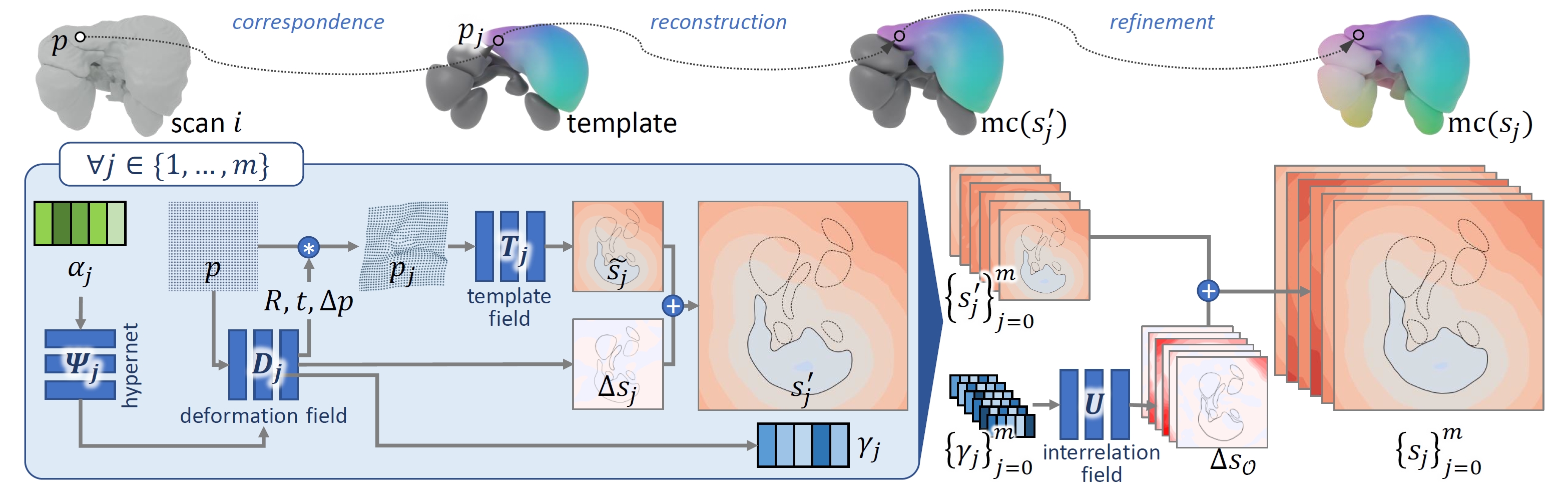
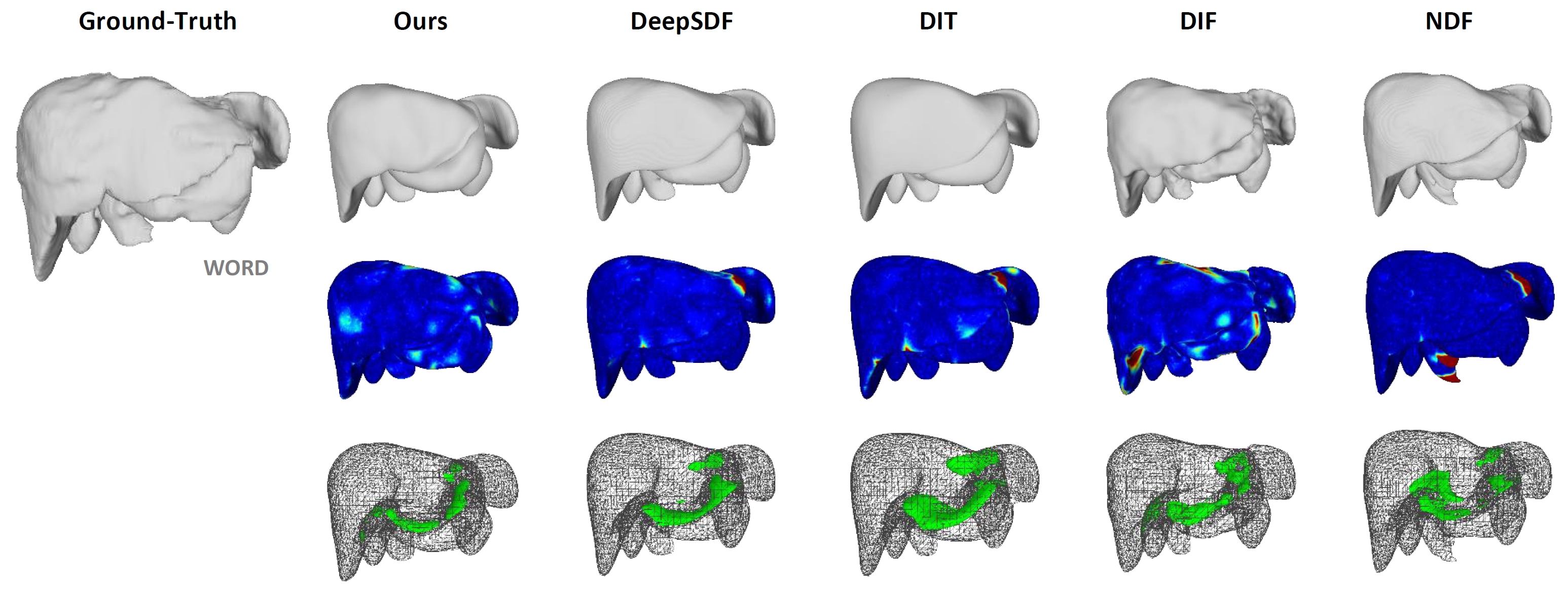
Yuchun Liu, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Zhongpai Gao, Pierre Sibut-Bourde, Fan Yang, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu, AAAI, 2024 We propose MODIF, a multi-object deep implicit function that jointly learns the deformation fields and instance-specific latent codes for multiple objects at once. Our emphasis is on non-rigid, non-interpenetrating entities such as organs. To effectively capture the interrelation between these entities and ensure precise, collision-free representations, our approach facilitates signaling between category-specific fields to adequately rectify shapes. We also introduce novel inter-object supervision: an attraction-repulsion loss is formulated to refine contact regions between objects. Our approach is demonstrated on various medical benchmarks, involving modeling different groups of intricate anatomical entities. |
|
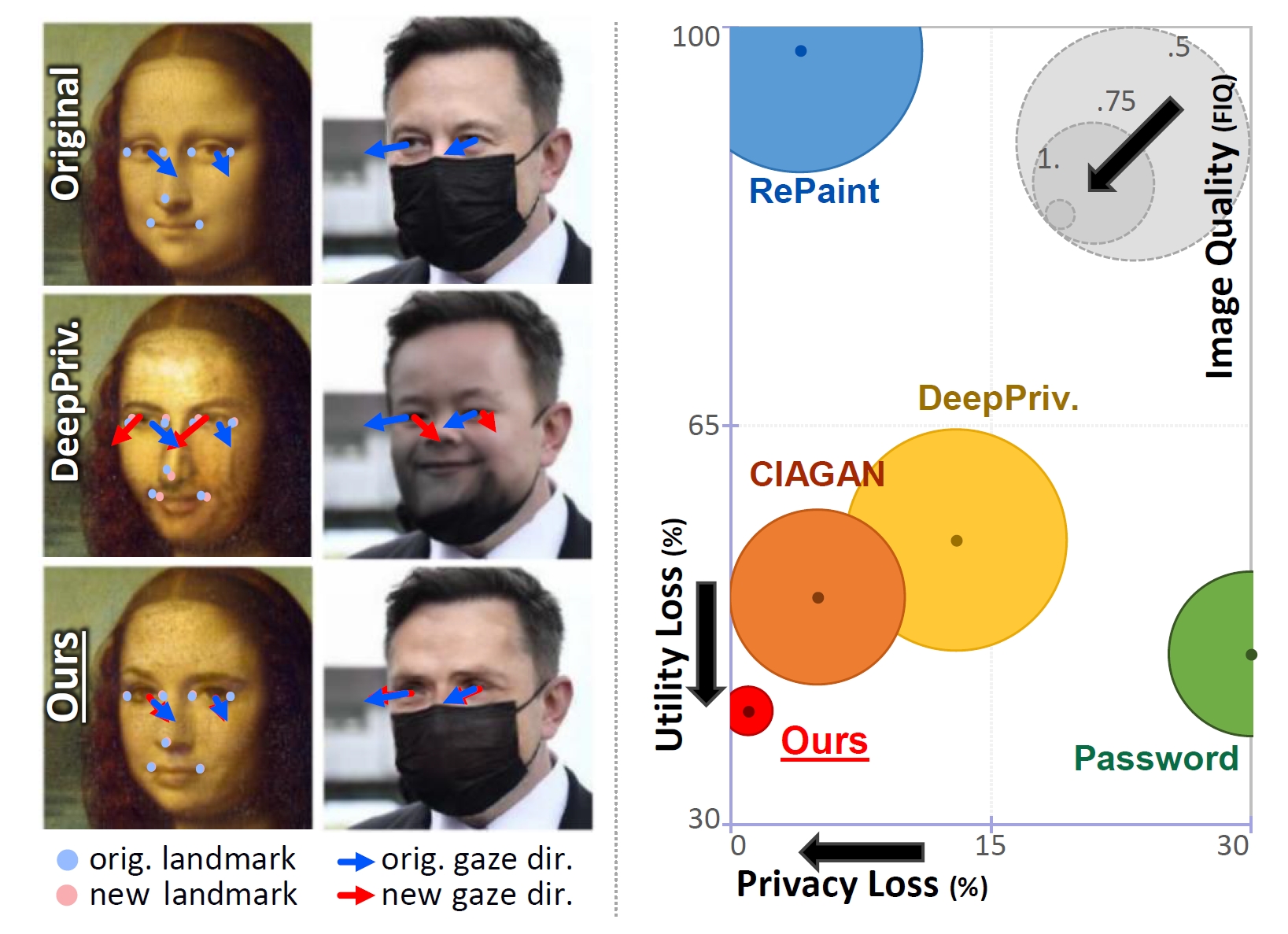
Zikui Cai, Zhongpai Gao Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Terrence Chen, M. Salman Asif, Ziyan Wu, AAAI, 2024 We introduce Disguise, a novel algorithm that seamlessly de-identifies facial images while ensuring the usability of the modified data. Unlike previous approaches, our solution is firmly grounded in the domains of differential privacy and ensemble-learning research. Our method involves extracting and substituting depicted identities with synthetic ones, generated using variational mechanisms to maximize obfuscation and non-invertibility. Additionally, we leverage supervision from a mixture-of-experts to disentangle and preserve other utility attributes. |
|
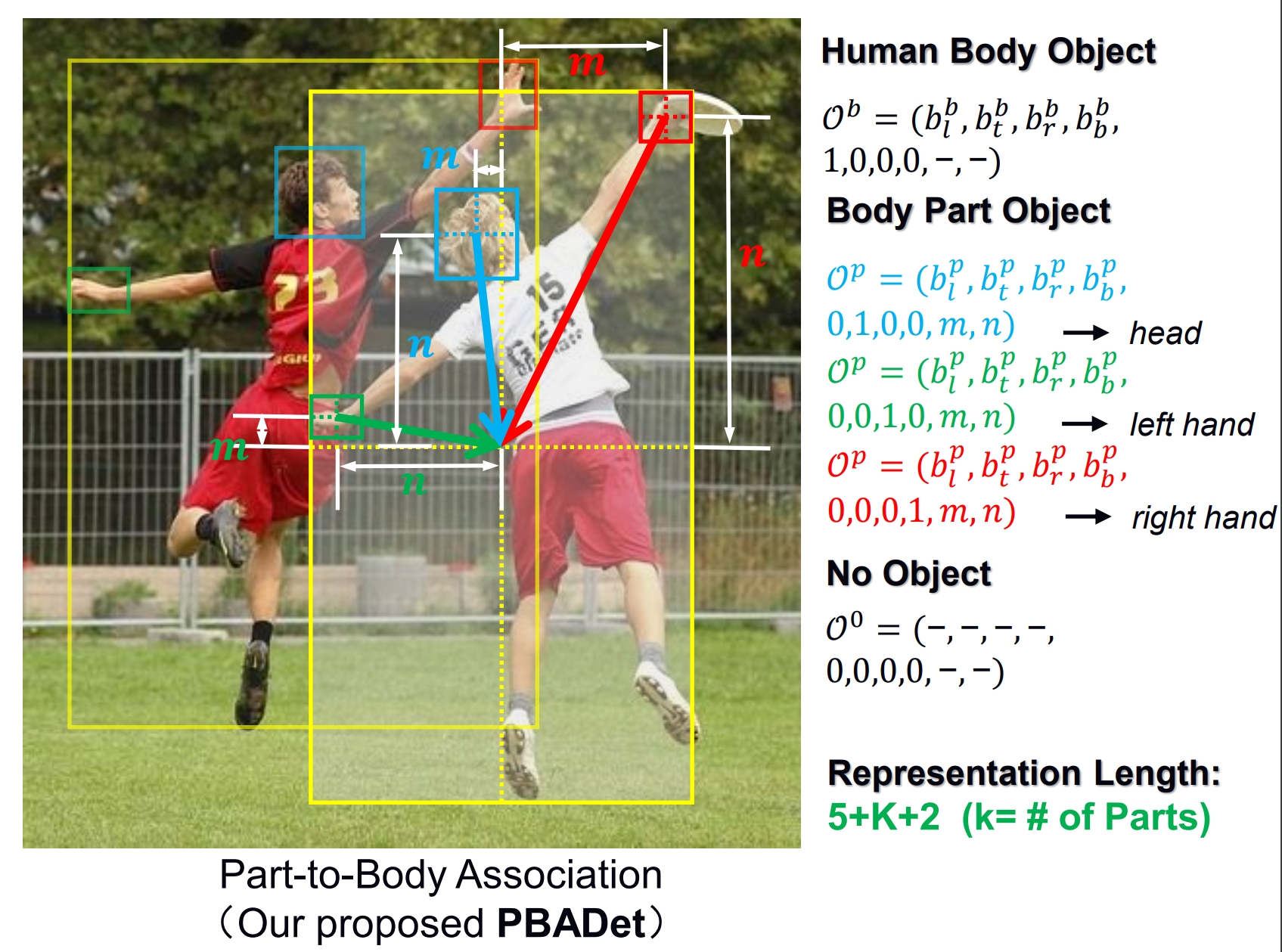
Zhongpai Gao, Huayi Zhou, Abhishek Sharma, Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu ICLR, 2024 This paper presents PBADet, a novel one-stage, anchor-free approach for part-body association detection. Building upon the anchor-free object representation across multi-scale feature maps, we introduce a singular part-to-body center offset that effectively encapsulates the relationship between parts and their parent bodies. Our design is inherently versatile and capable of managing multiple parts-to-body associations without compromising on detection accuracy or robustness. Comprehensive experiments on various datasets underscore the efficacy of our approach, which not only outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques but also offers a more streamlined and efficient solution to the part-body association challenge. |
|
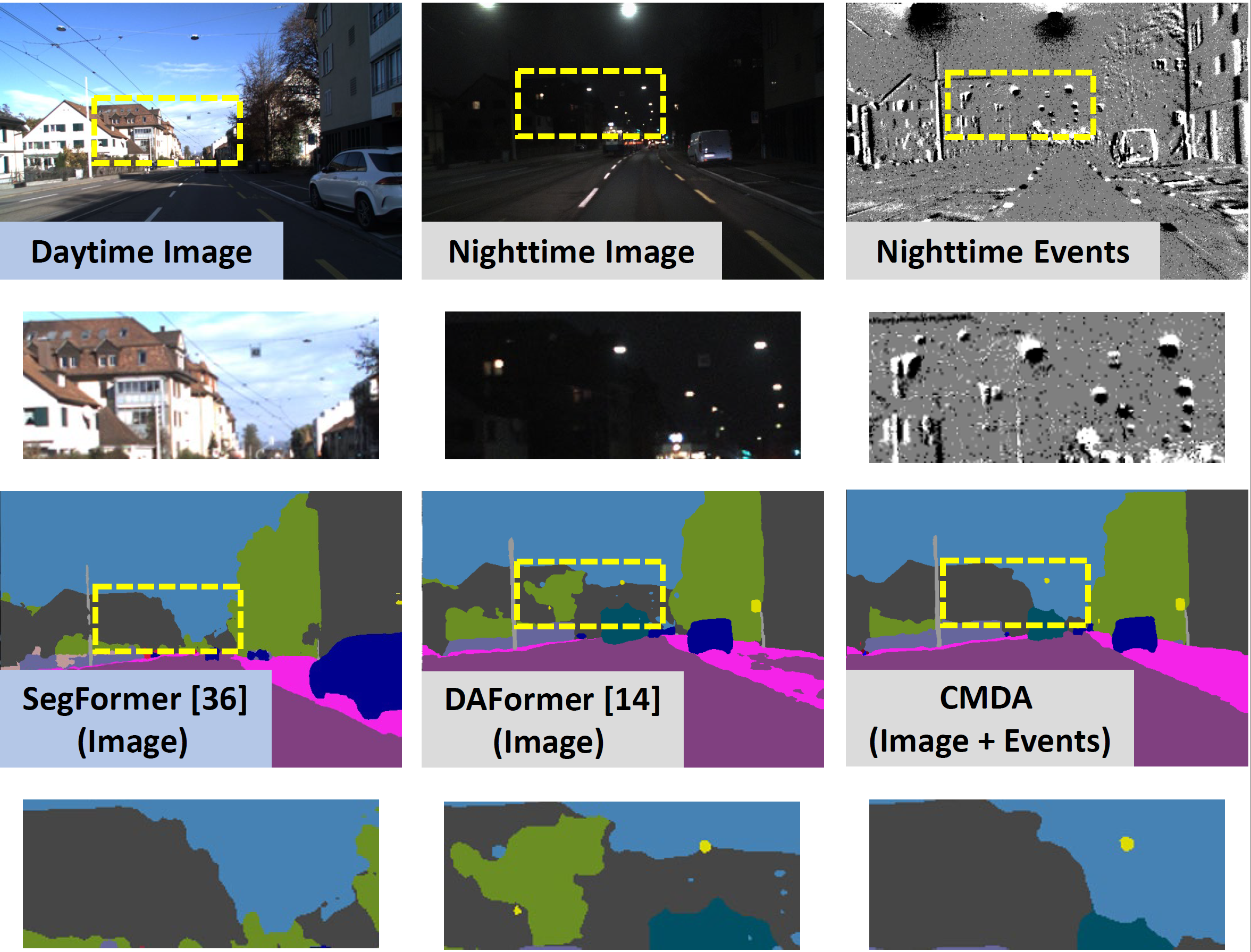
Ruihao Xia, Chaoqiang Zhao, Meng Zheng, Ziyan Wu, Qiyu Sun, Yang Tang ICCV, 2023 We propose a novel unsupervised Cross-Modality Domain Adaptation (CMDA) framework to leverage multi-modality (Images and Events) information for nighttime semantic segmentation, with only labels on daytime images. In CMDA, we design the Image Motion-Extractor to extract motion information and the Image Content-Extractor to extract content information from images, in order to bridge the gap between different modalities (Images <=> Events) and domains (Day <=> Night). Besides, we introduce the first image-event nighttime semantic segmentation dataset. |
|
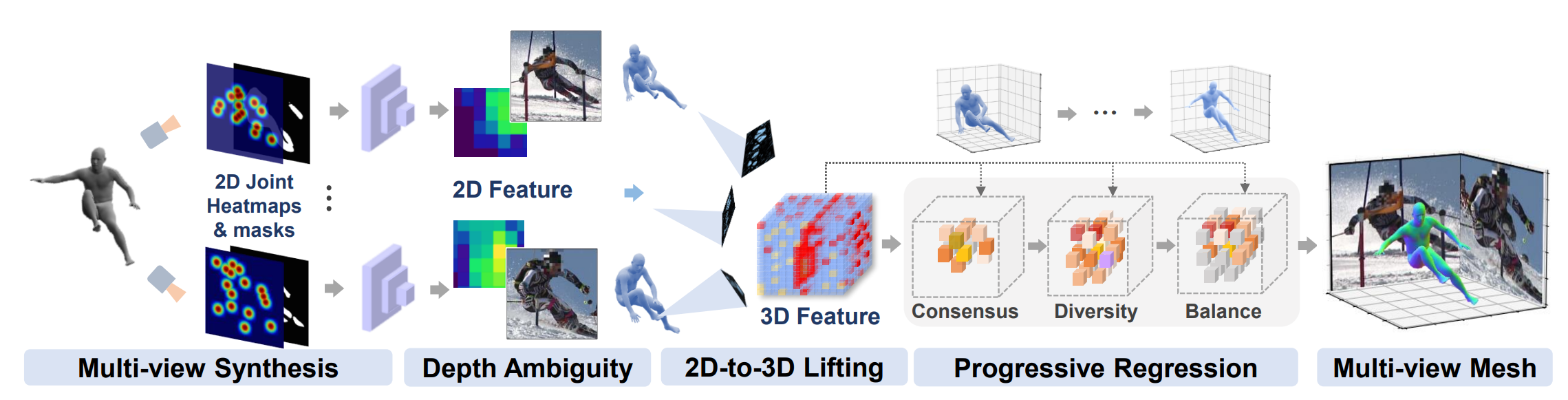
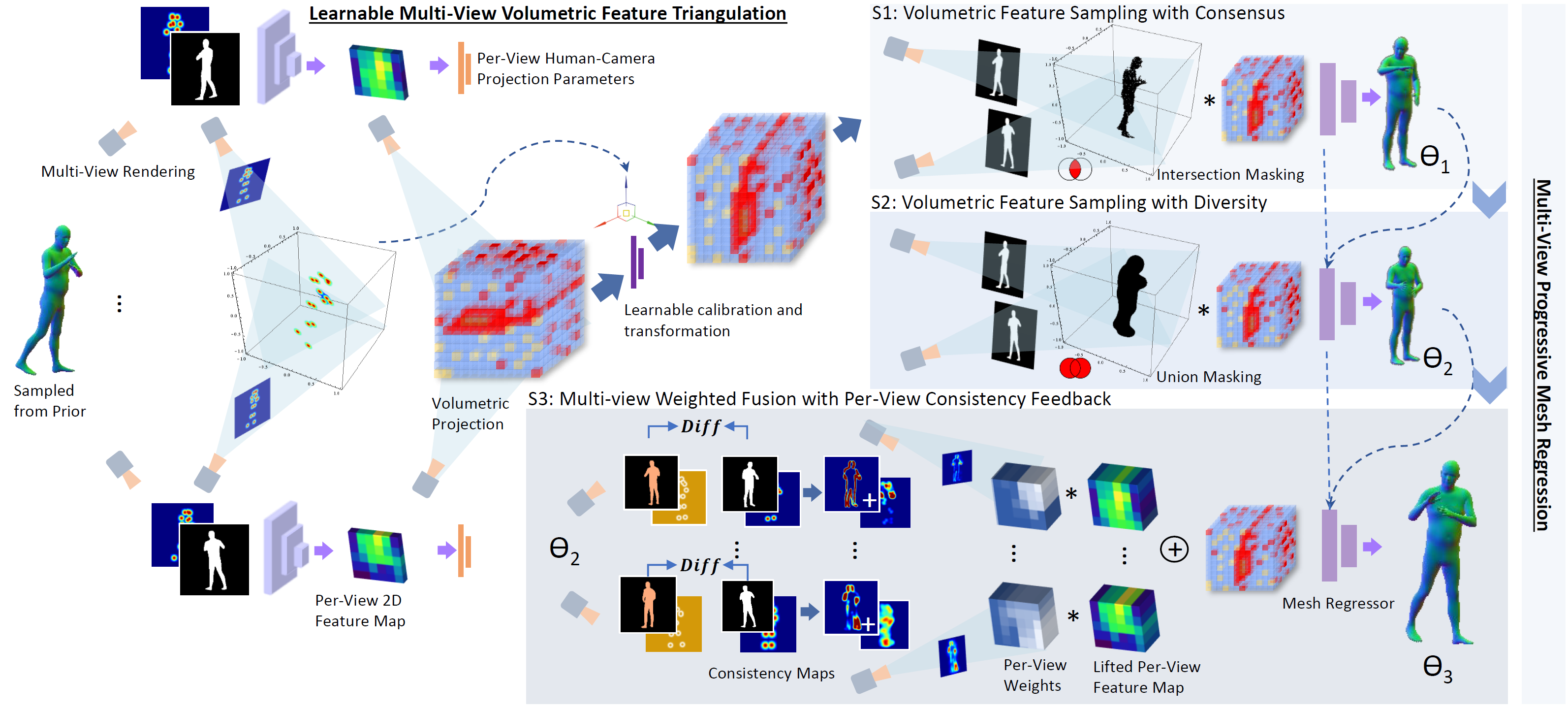
Xuan Gong, Liangcheng Song, Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Terrence Chen, Junsong Yuan, David Doermann, Ziyan Wu AAAI (oral), 2023 A novel simulation-based training pipeline for multi-view human mesh recovery, which (a) relies on intermediate 2D representations which are more robust to synthetic-to-real domain gap; (b) leverages learnable calibration and triangulation to adapt to more diversified camera setups; and (c) progressively aggregates multi-view information in a canonical 3D space to remove ambiguities in 2D representations. |
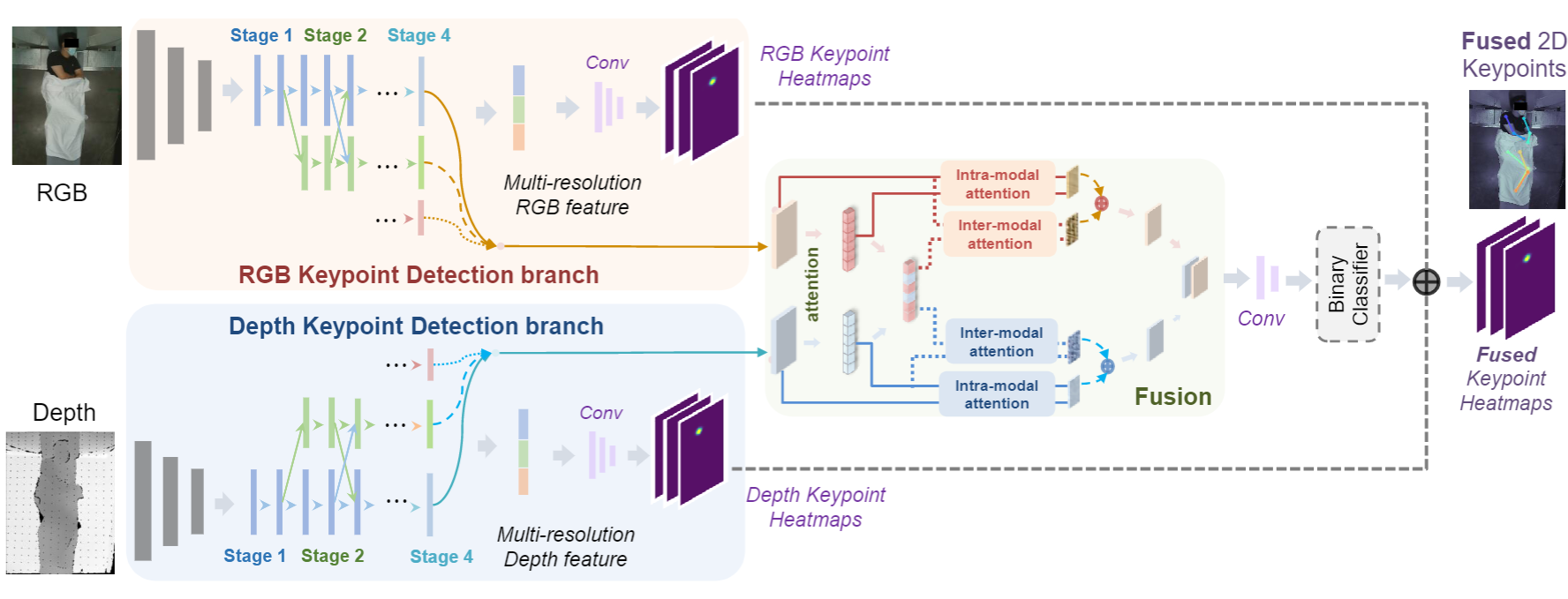
|
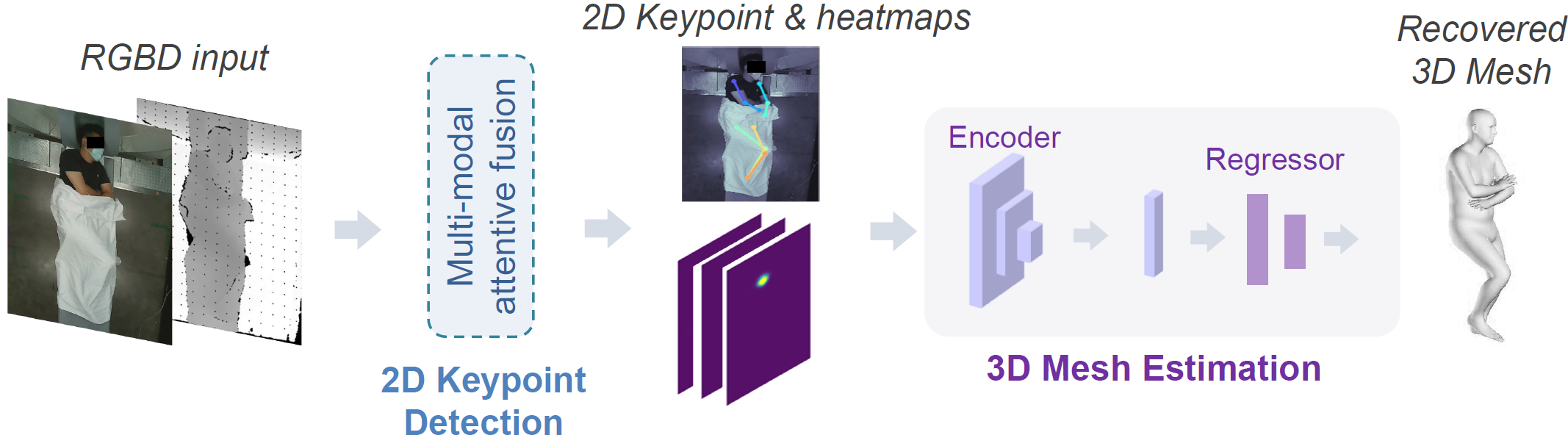
Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Xuan Gong, Fan Yang, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu MICCAI (early accept), 2022 A generic modularized 3D patient modeling method consists of (a) a multi-modal keypoint detection module with attentive fusion for 2D patient joint localization, to learn complementary cross-modality patient body information, leading to improved keypoint localization robustness and generalizability in a wide variety of imaging and clinical scenarios; and (b) a self-supervised 3D mesh regression module which does not require expensive 3D mesh parameter annotations to train, bringing immediate cost benefits for clinical deployment. |
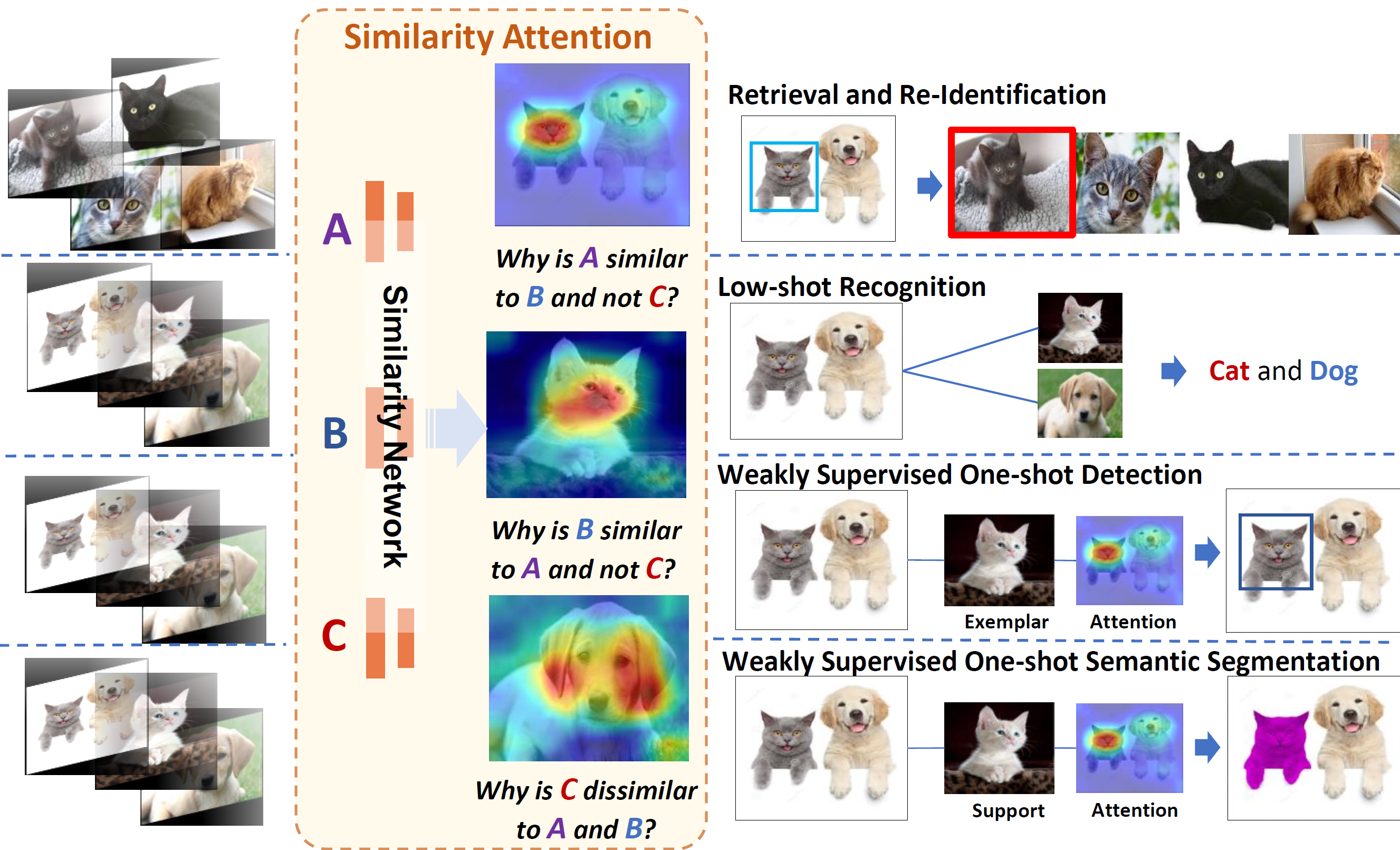
|
Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu, Richard J. Radke IJCAI, 2022 A novel method to generate generic visual similarity explanations with gradient-based attention. It is agnostic to the specific similarity model type, e.g., we show applicability to Siamese, triplet, and quadruplet models. Furthermore, we make our proposed similarity attention a principled part of the learning process, resulting in a new paradigm for learning similarity functions. We demonstrate that our learning mechanism results in more generalizable, as well as explainable, similarity models. |
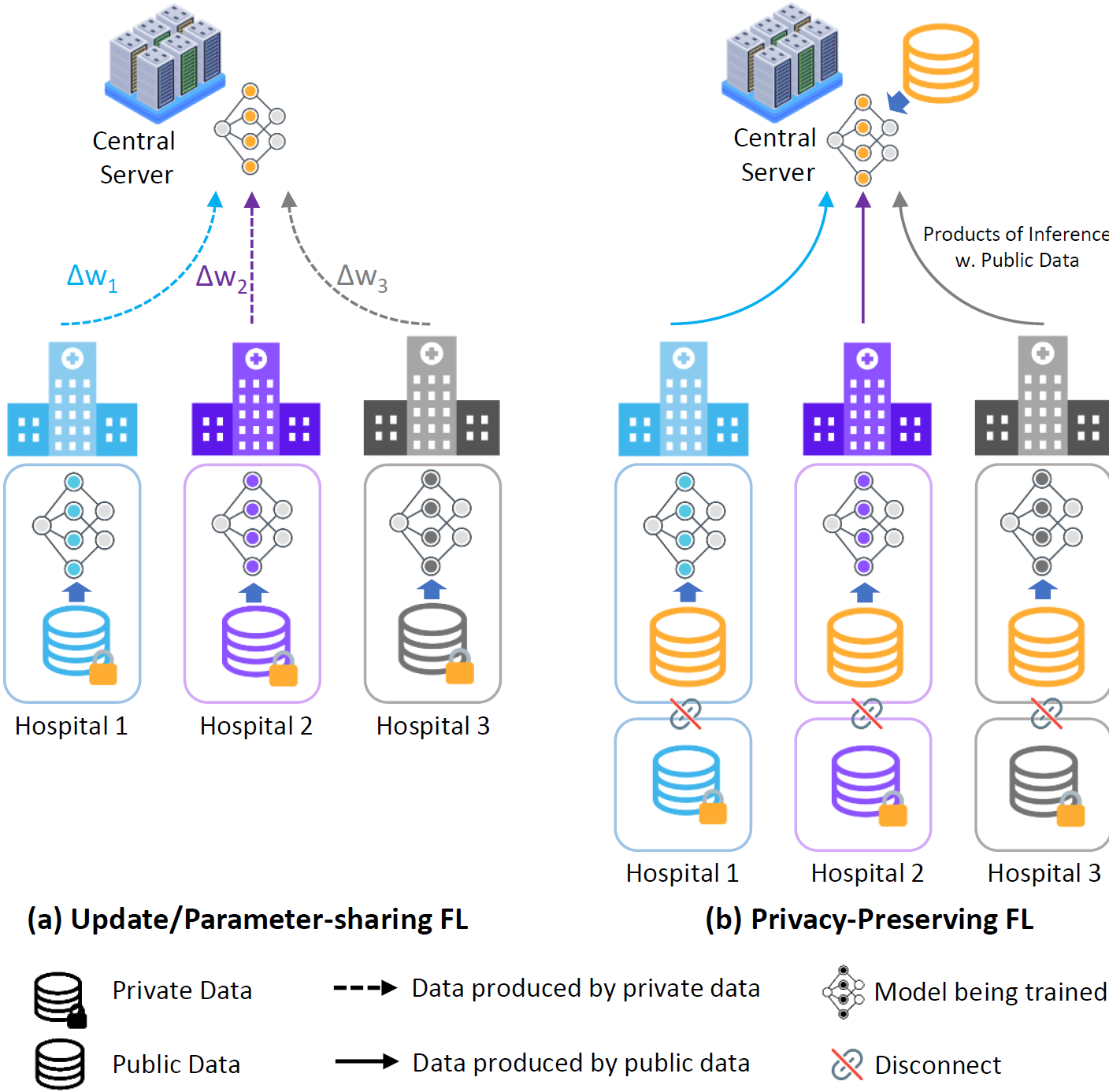
|
Xuan Gong, Liangcheng Song, Rishi Vedula, Abhishek Sharma, Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Arun Innanje, Terrence Chen, Junsong Yuan, David Doermann, Ziyan Wu IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2023 A privacy-preserving FL framework leveraging unlabeled public data for one-way offline knowledge distillation. The central model is learned from local knowledge via ensemble attention distillation. Our technique uses decentralized and heterogeneous local data like existing FL approaches, but more importantly, it significantly reduces the risk of privacy leakage. |
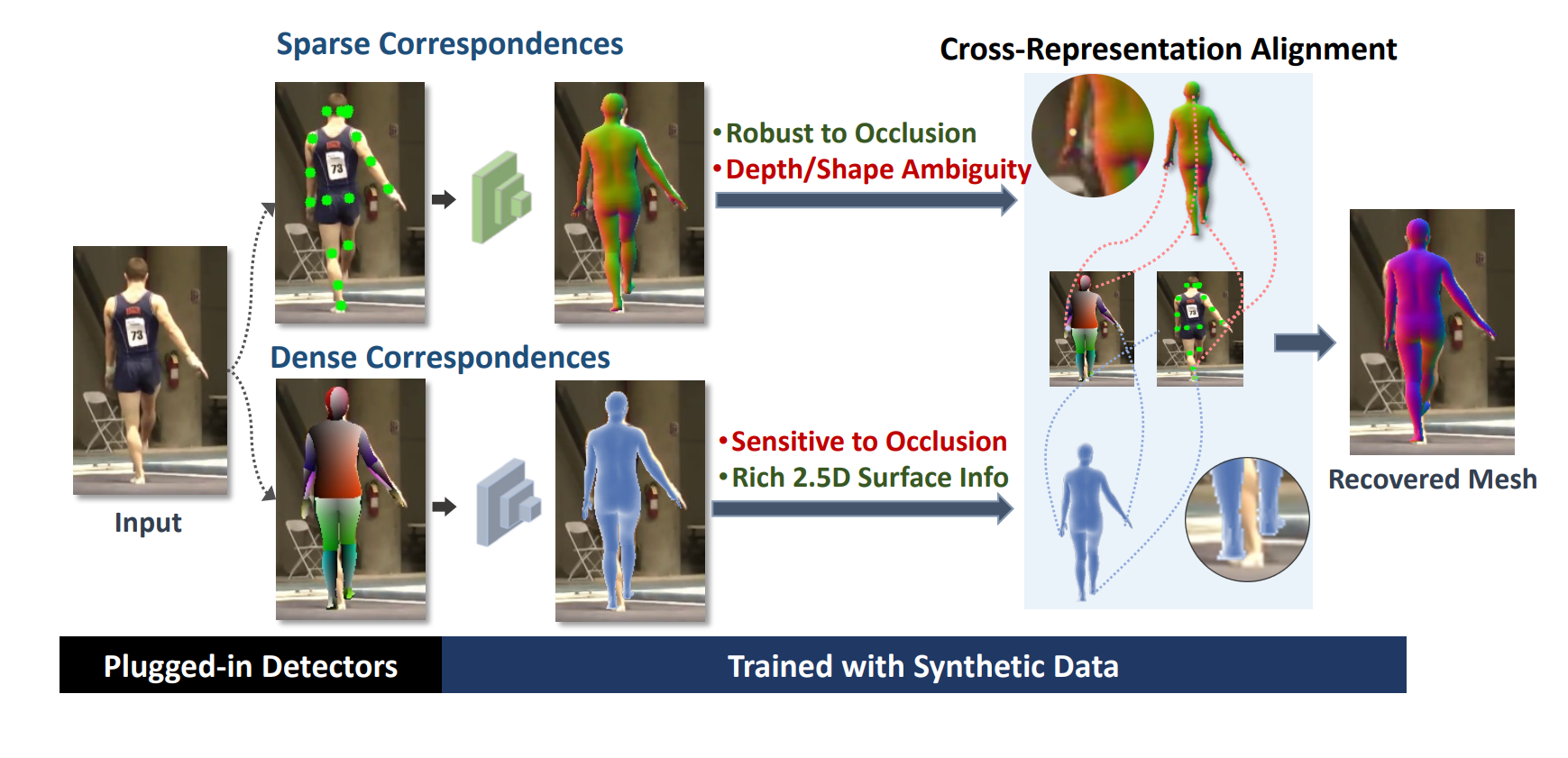
|
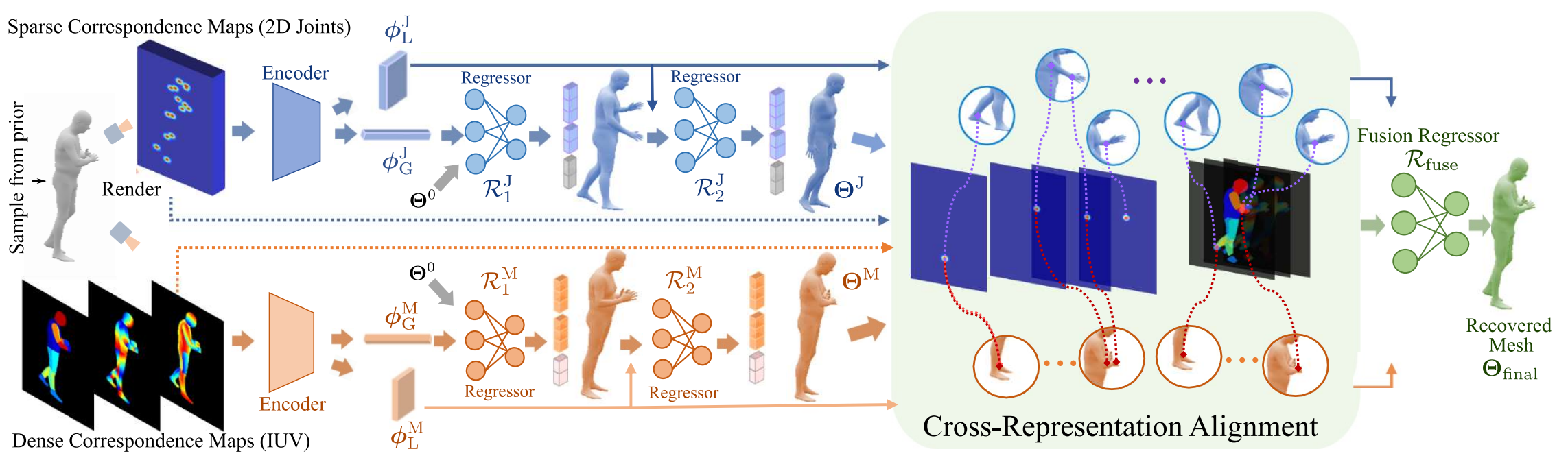
Xuan Gong, Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Srikrishna Karanam, Terrence Chen, David Doermann, Ziyan Wu ECCV, 2022 A Cross-representation alignment technique utilizing the complementary information from the robust but sparse representation (2D keypoints) for self-supervised human mesh recovery. Specifically, the alignment errors between initial mesh estimation and both 2D representations are forwarded into regressor and dynamically corrected in the following mesh regression. This adaptive cross-representation alignment explicitly learns from the deviations and captures complementary information: robustness from sparse representation and richness from dense representation. |
|
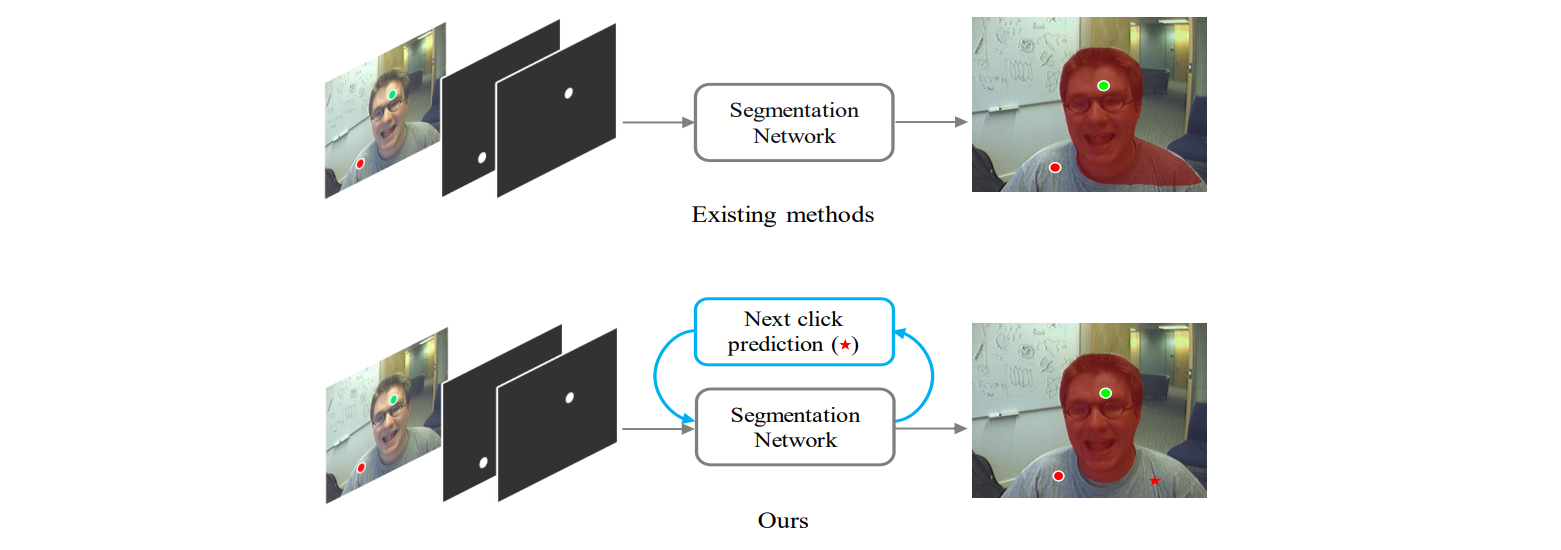
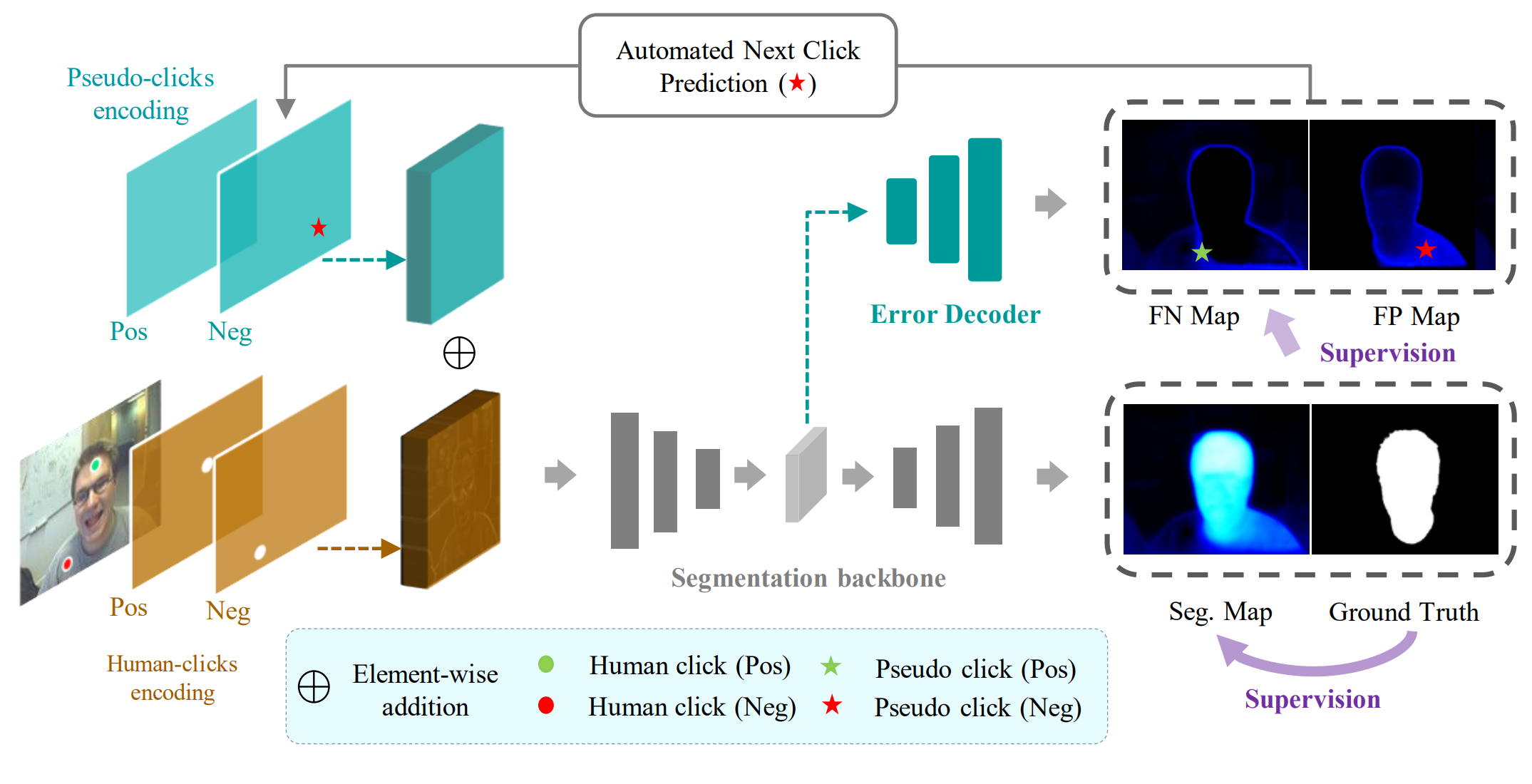
Qin Liu, Meng Zheng, Benjamin Planche, Srikrishna Karanam, Terrence Chen, Marc Niethammer, Ziyan Wu ECCV, 2022 A generic framework that enables existing segmentation networks to propose candidate next clicks. These automatically generated clicks, termed pseudo clicks in this work, serve as an imitation of human clicks to refine the segmentation mask. We build PseudoClick on existing segmentation backbones and show how the click prediction mechanism leads to improved performance. |
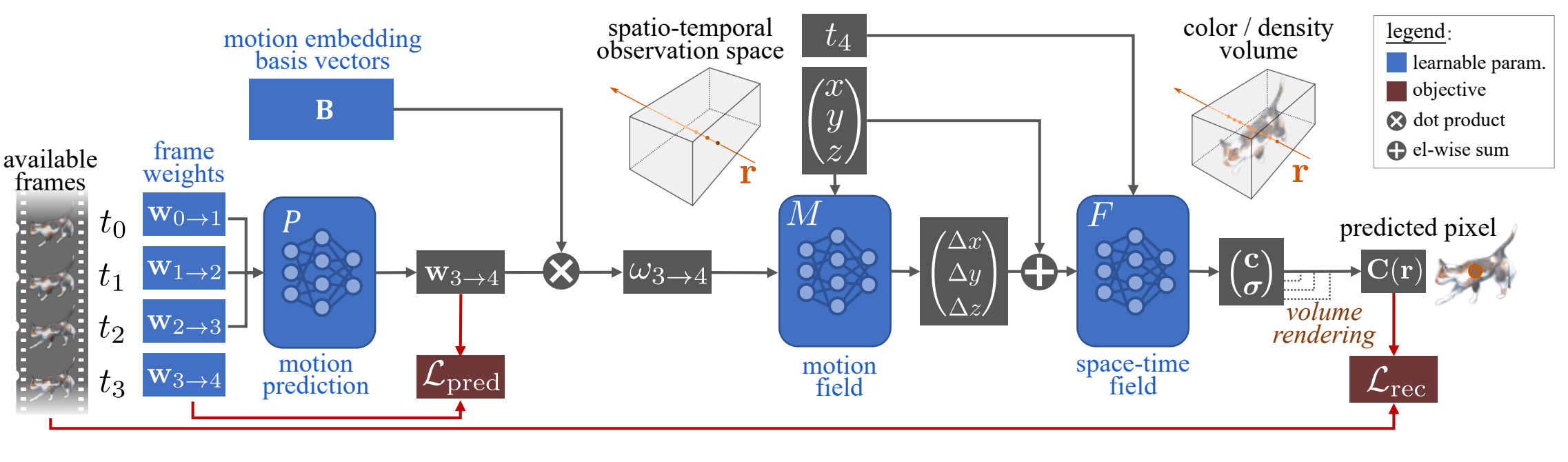
|
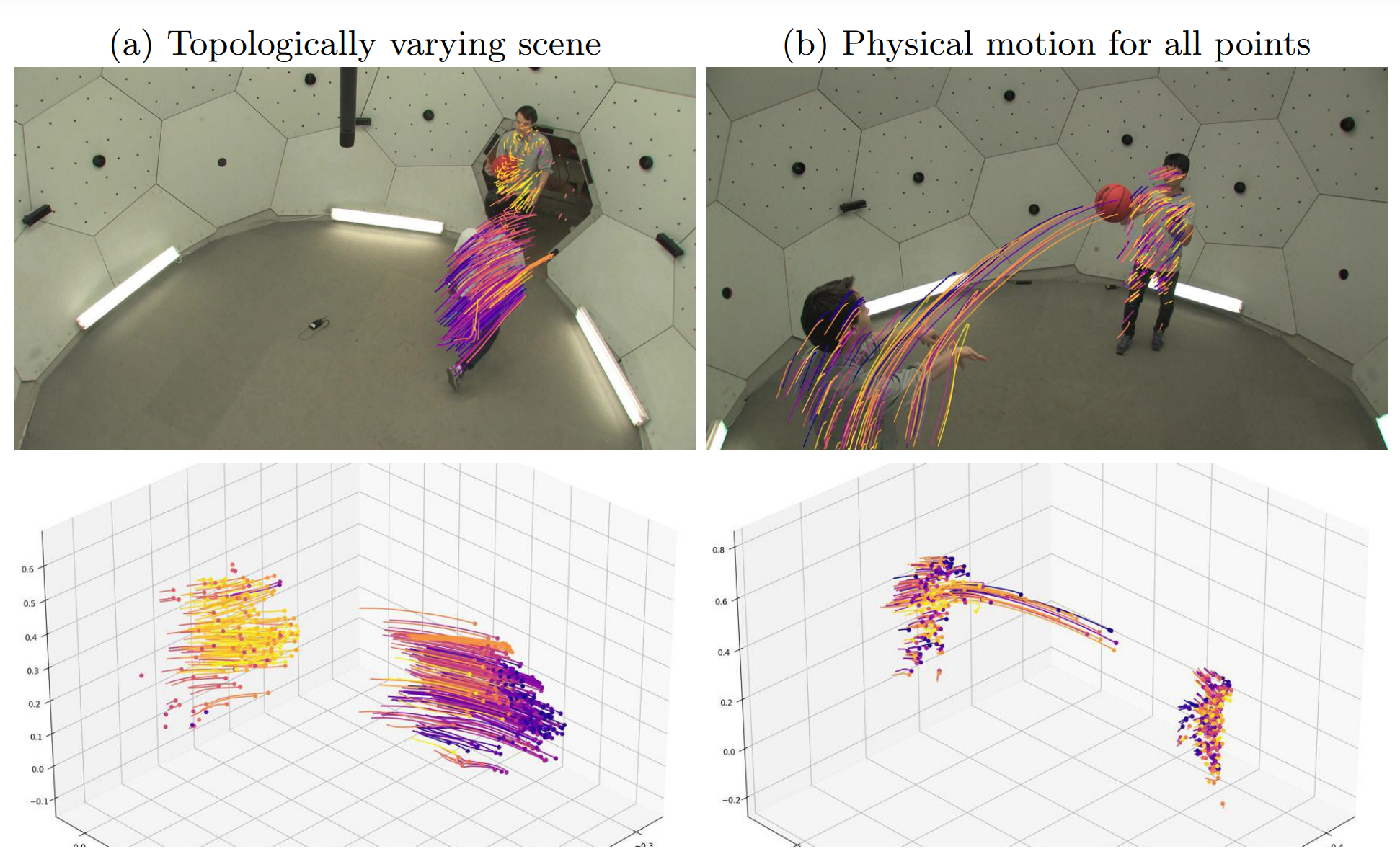
Liangcheng Song, Xuan Gong, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, David Doermann, Junsong Yuan, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu ECCV (oral), 2022 A predictability regularization by first conditioning the estimated motion on latent embeddings, then by adopting a predictor network to enforce predictability on the embeddings. We propose to regularize the estimated motion to be predictable. If the motion from previous frames is known, then the motion in the near future should be predictable. |
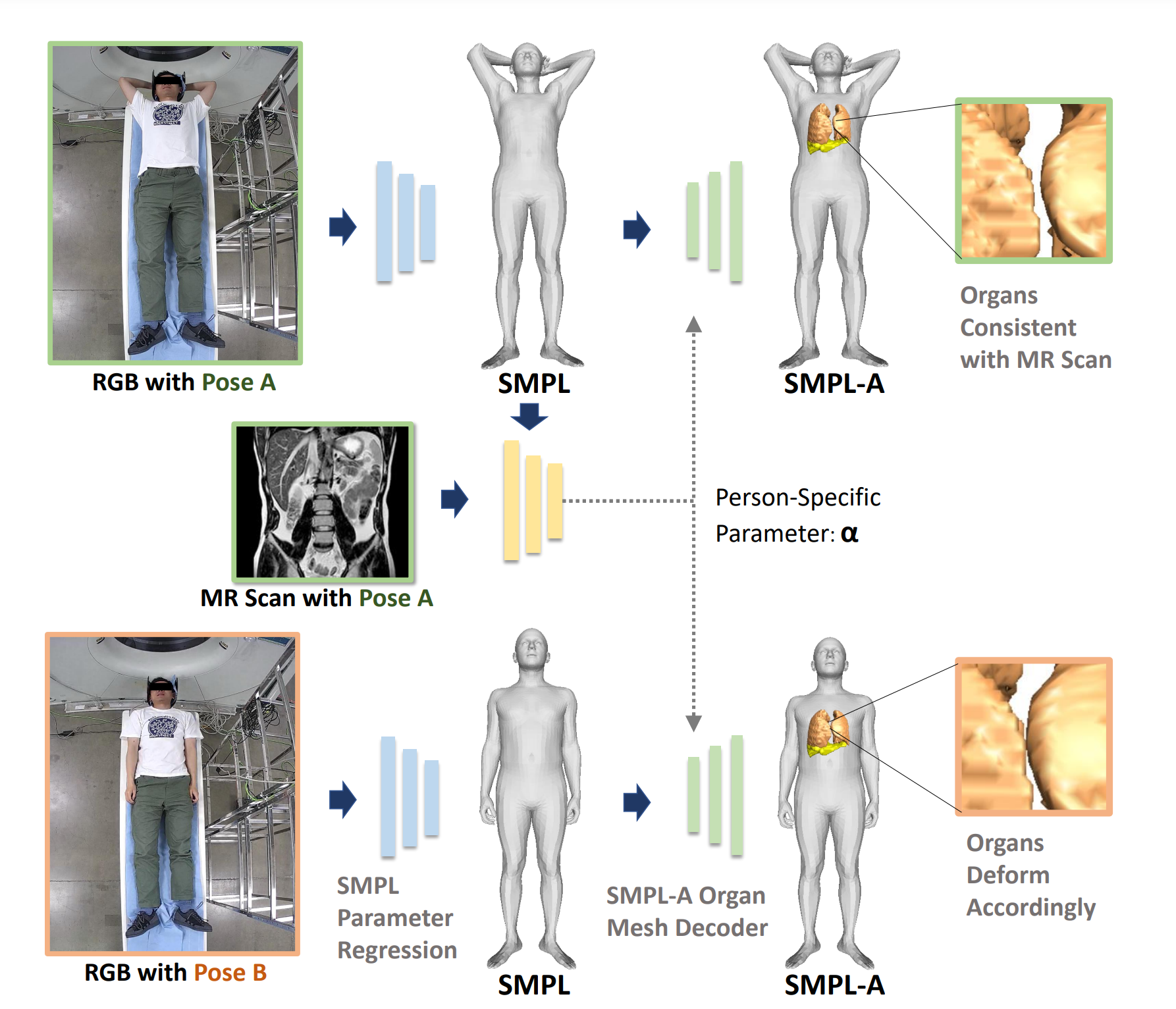
|
Hengtao Guo, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu CVPR, 2022 A novel learning-based approach to estimate the patient's internal organ deformation for arbitrary human poses in order to assist with radiotherapy and similar medical protocols. The underlying method first leverages medical scans to learn a patient-specific representation that potentially encodes the organ's shape and elastic properties. During inference, given the patient's current body pose information and the organ's representation extracted from previous medical scans, our method can estimate their current organ deformation to offer guidance to clinicians. |
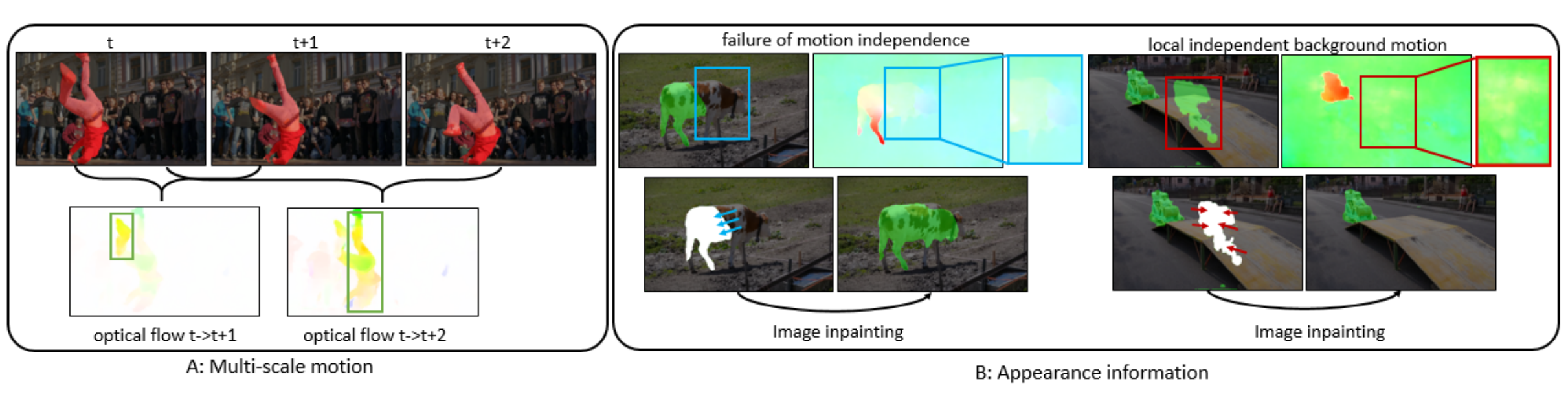
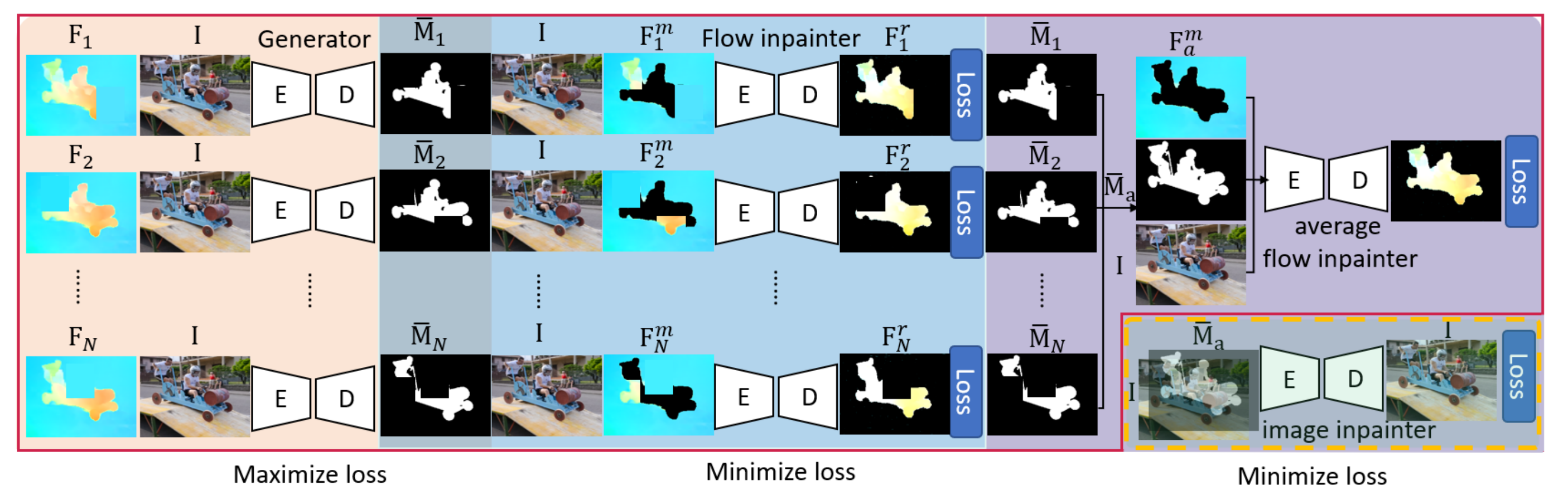
|
Fan Yang, Srikrishna Karanam, Meng Zheng, Terrence Chen, Haibin Ling, Ziyan Wu WACV, 2022 A Multimotion and Appearance Self-supervised Network (MASNet) to introduce multi-scale motion information and appearance information of scene for MOD. To encode multi-scale motion and appearance, in MASNet we respectively design a multi-branch flow encoding module and an image inpainter module. |
|
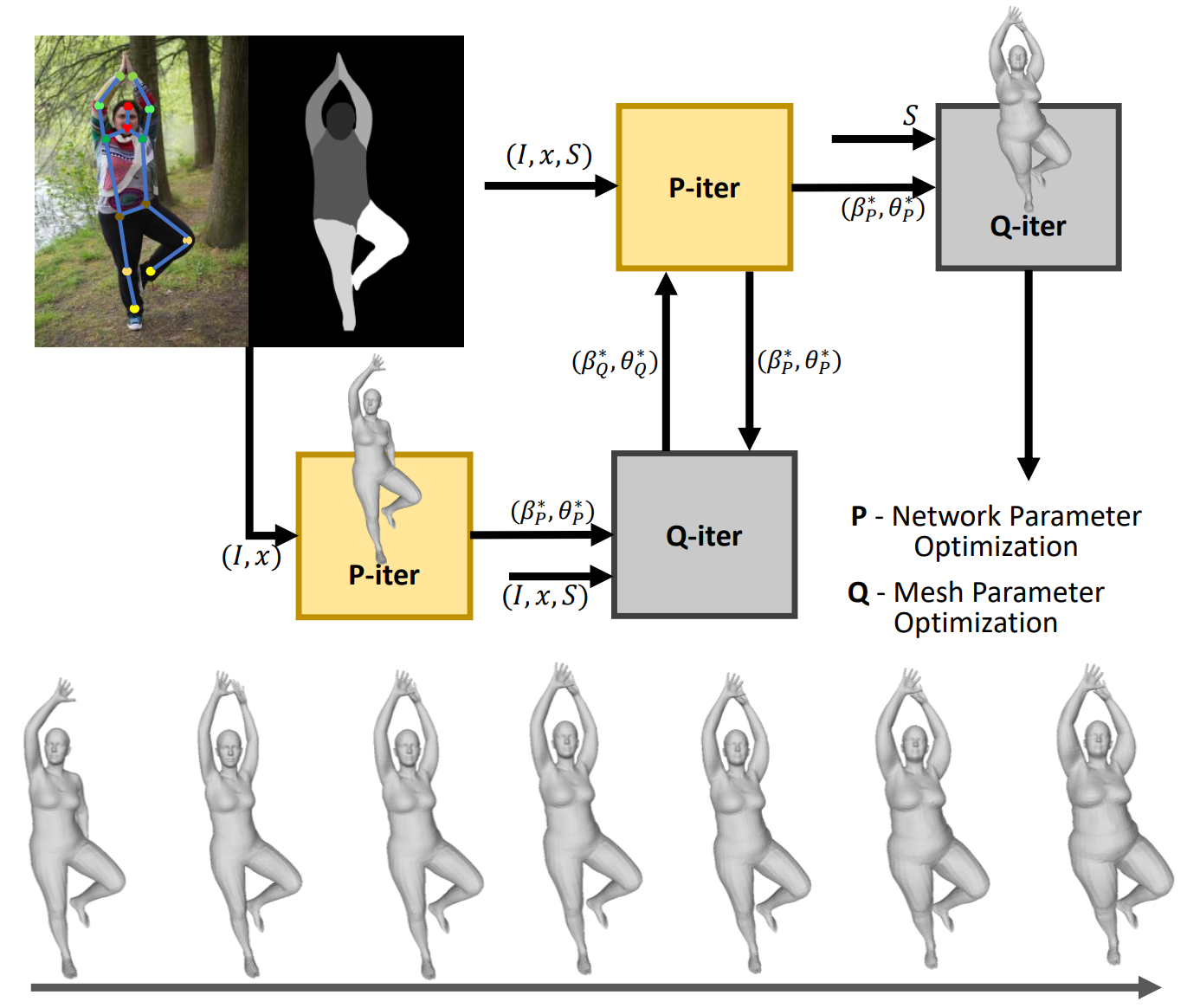
Ren Li, Srikrishna Karanam, Meng Zheng, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu BMVC (oral), 2021 A solution to the problem of obese human mesh recovery, i.e., fitting a parametric human mesh to images of obese people. We present a simple baseline that is scalable and can be easily used in conjunction with existing algorithms to improve their performance. We also present a generalized human mesh optimization algorithm that substantially improves the performance of existing methods on both obese person images as well as community-standard benchmark datasets. |
|
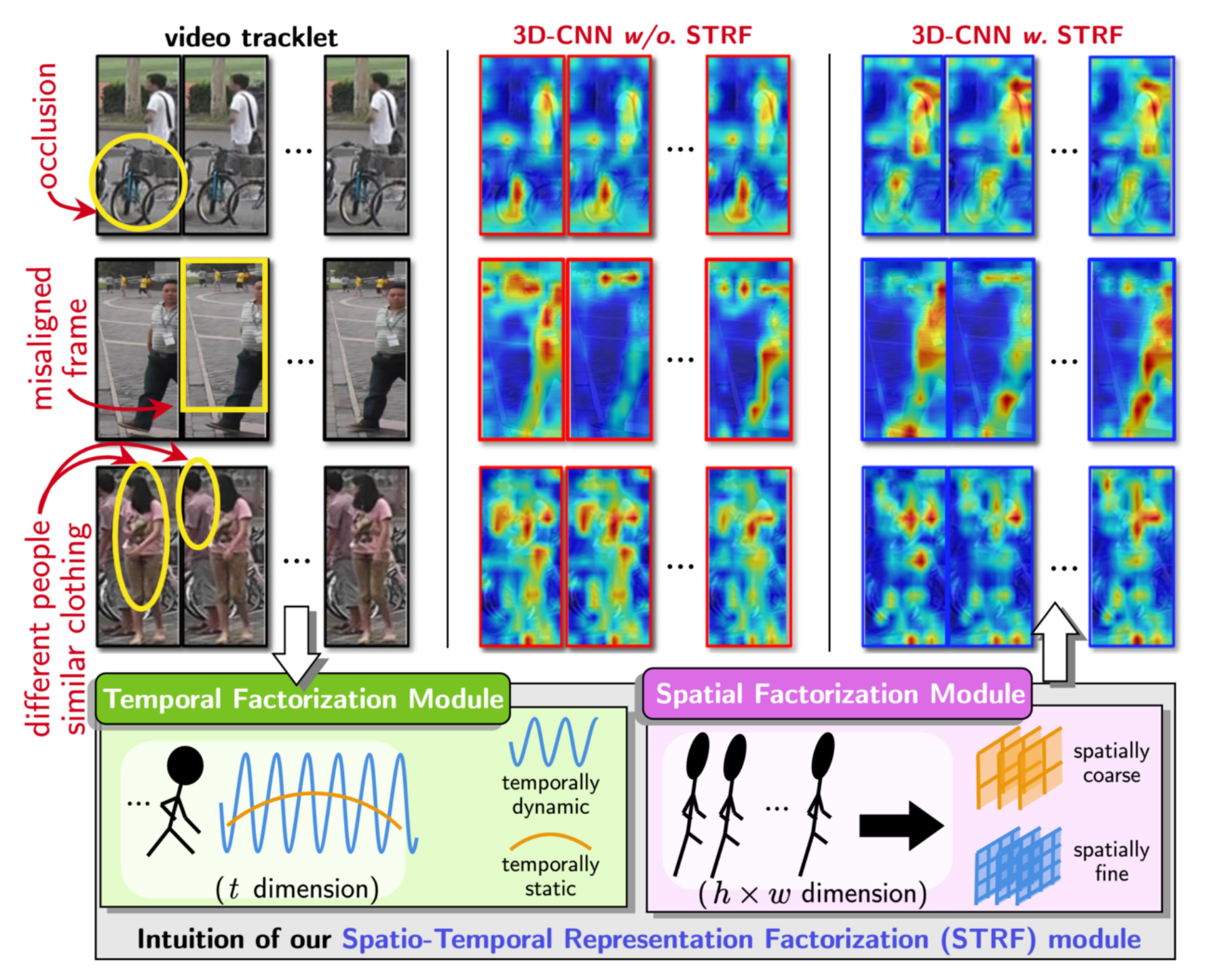
Abhishek Aich, Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu ICCV, 2021 A flexible new computational unit that can be used in conjunction with most existing 3D convolutional neural network architectures for re-ID. The key innovations of the proposed STRF over prior work include explicit pathways for learning discriminative temporal and spatial features, with each component further factorized to capture complementary person-specific appearance and motion information. |
|
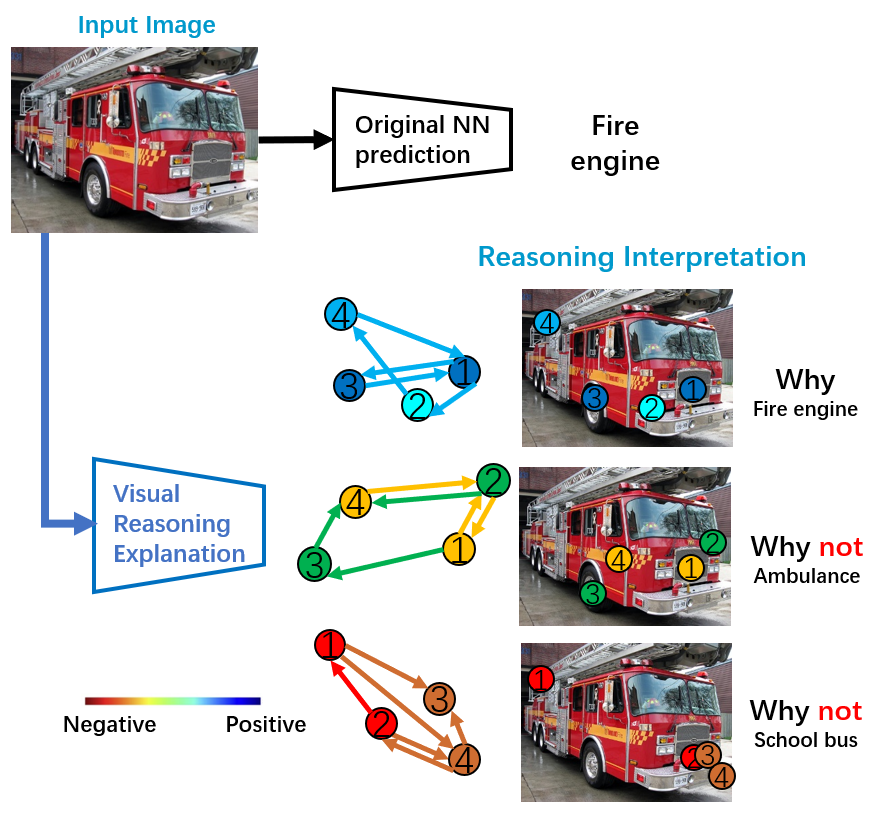
Yunhao Ge, Yao Xiao, Zhi Xu, Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Terrence Chen, Laurent Itti, Ziyan Wu CVPR, 2021 A framework (VRX) to interpret classification NNs with intuitive structural visual concepts. Given a trained classification model, VRX extracts relevant class-specific visual concepts and organizes them using structural concept graphs (SCG) based on pairwise concept relationships. By means of knowledge distillation, we show VRX can take a step towards mimicking the reasoning process of NNs and provide logical, concept-level explanations for final model decisions. |
|
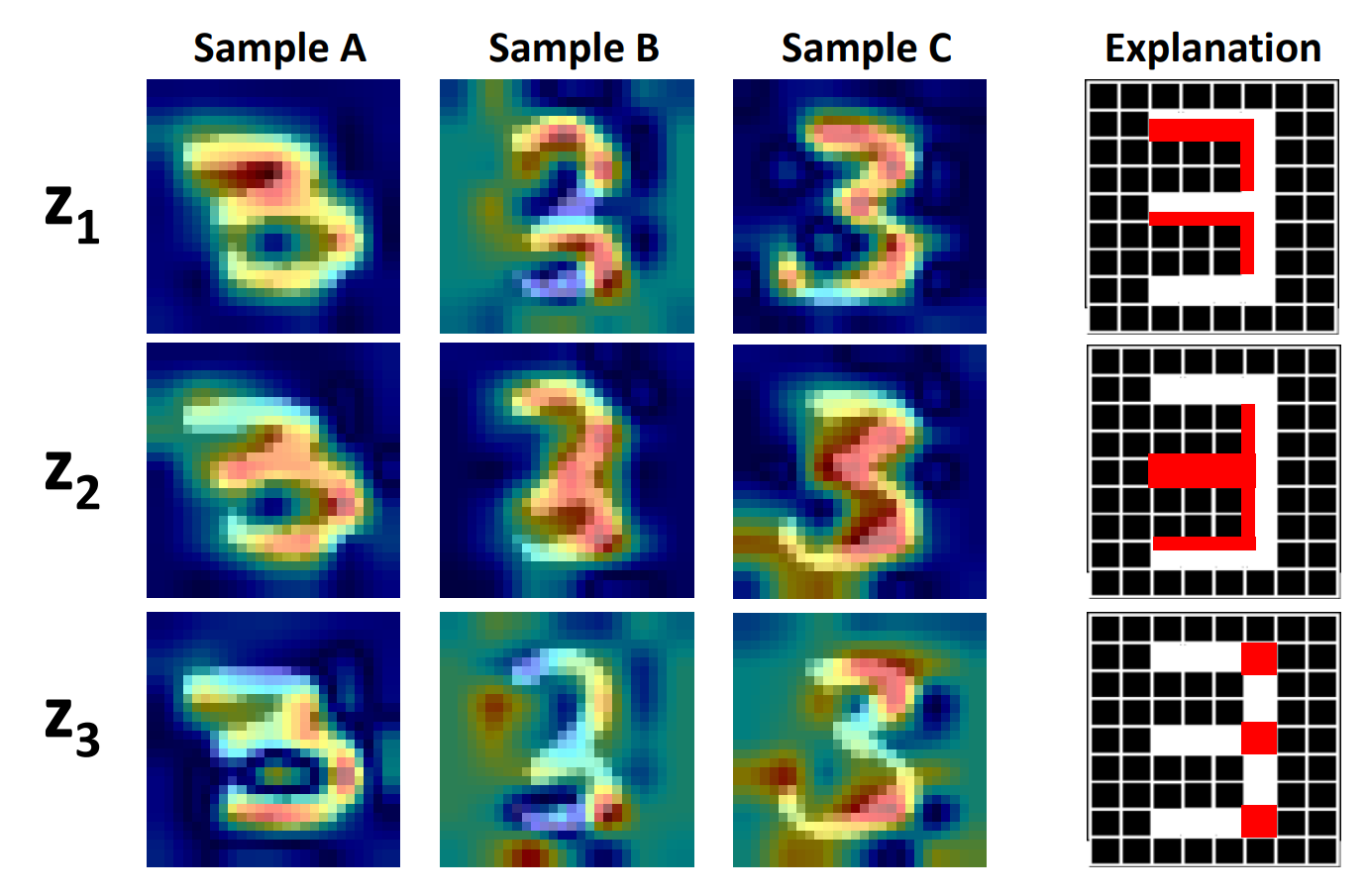
Wenqian Liu*, Runze Li*, Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Ziyan Wu, Bir Bhanu, Richard J. Radke, Octavia Camps CVPR, 2020 A novel technique to visually explain VAEs by means of gradient-based attention. We present methods to generate visual attention from the learned latent space, and also demonstrate such attention explanations serve more than just explaining VAE predictions. We show how these attention maps can be used to localize anomalies in images, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on the MVTec-AD dataset. |
|
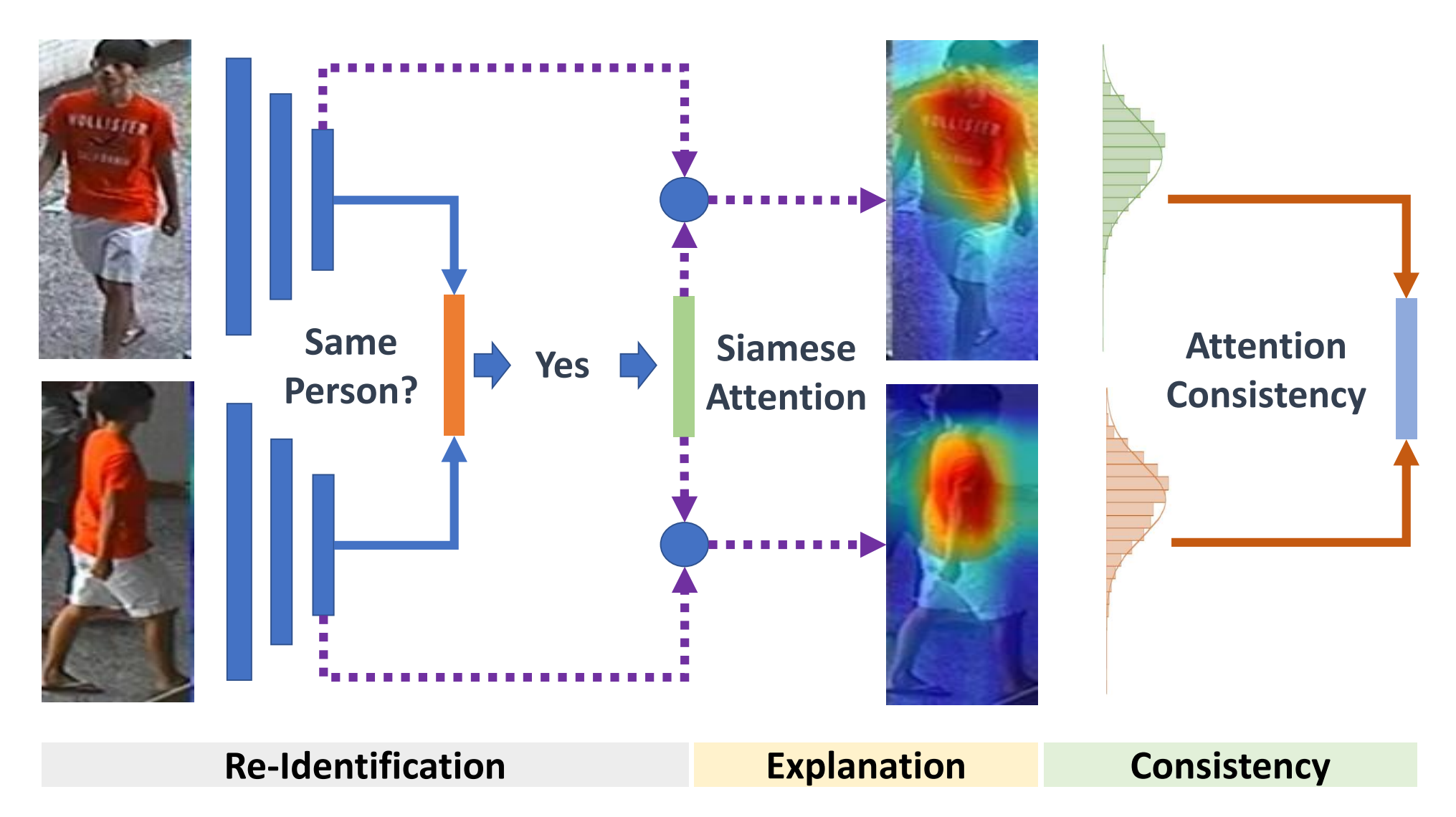
Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Ziyan Wu, Richard J. Radke CVPR, 2019 A framework for re-id that provides mechanisms to make attention and attention consistency end-to-end trainable in a Siamese learning architecture, resulting in a technique for robust cross-view matching as well as explaining the reasoning for why the model predicts that the two images belong to the same person |
|
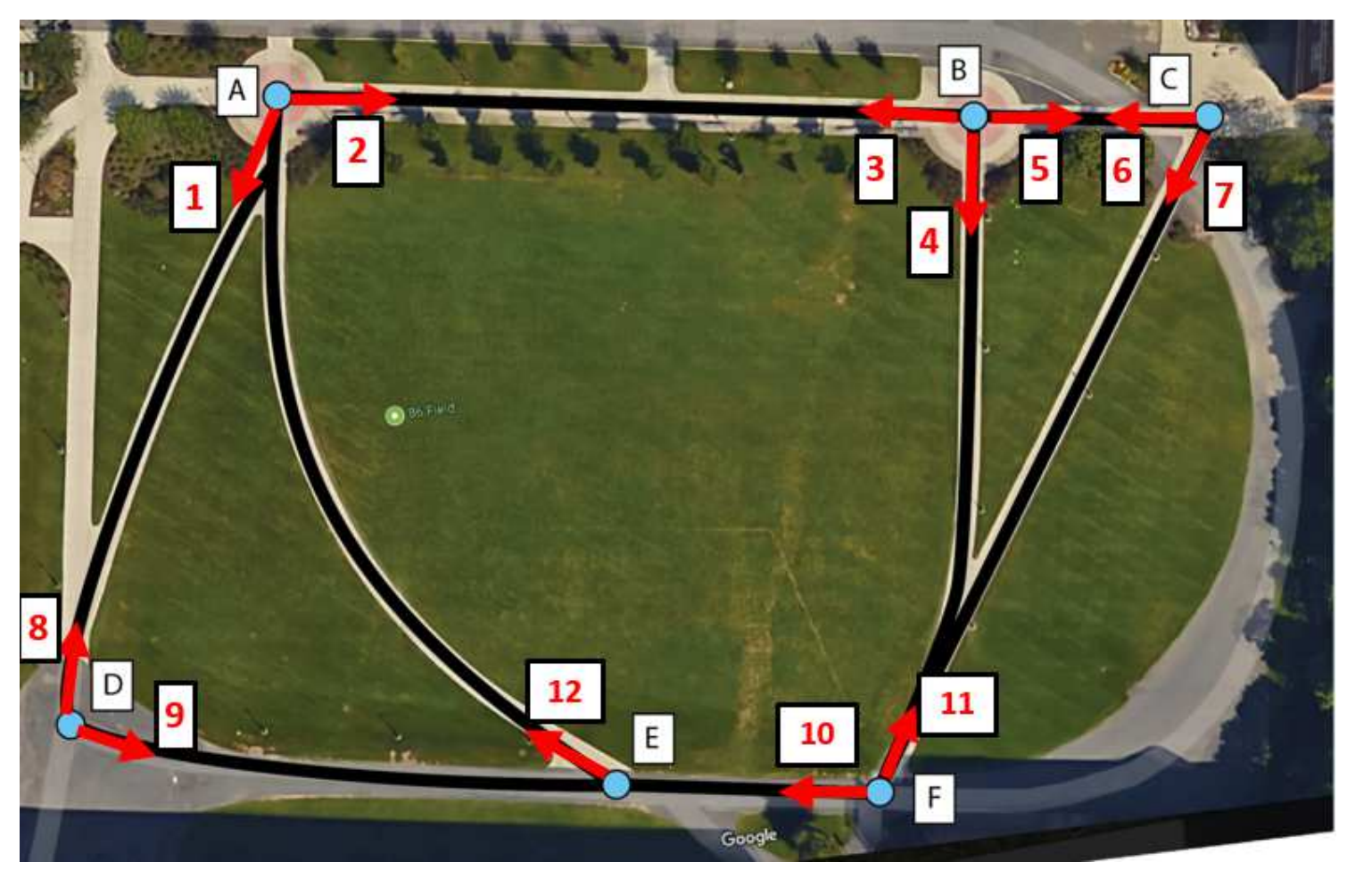
Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Richard J. Radke CVPR Workshop, 2018 A new multi-shot re-id dataset, called RPIfield, which provides explicit time-stamp information for each candidate. The RPIfield dataset is comprised of 12 outdoor camera videos, with 112 known actors walking along pre-specified paths among about 4000 distractors. Each actor in RPIfield has multiple reappearances in one or more camera views, which allows the study of re-id algorithms in a more general context, especially with respect to temporal aspects. |
|
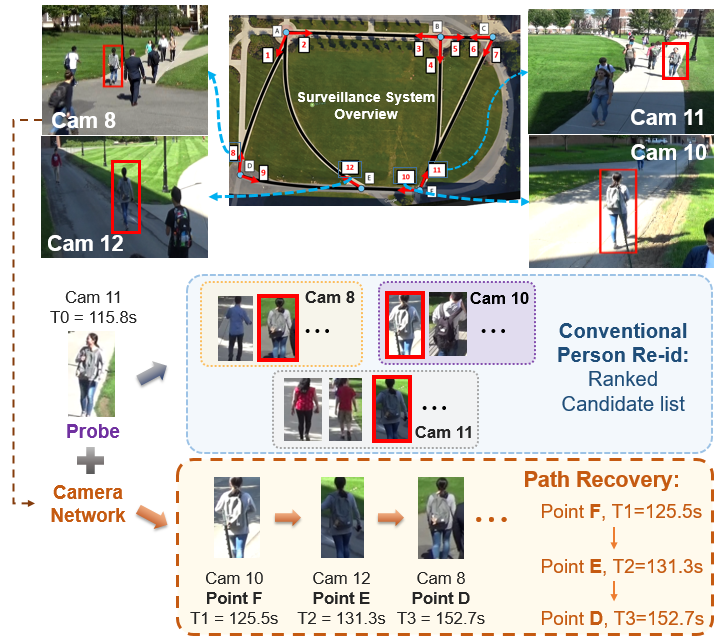
Meng Zheng, Srikrishna Karanam, Richard J. Radke IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 2020 A new algorithm to automatically reconstruct the time-stamped spatial trajectory of a person of interest moving in a camera network. With this output, a surveillance system user can easily tell where in the camera network the person of interest was located at any specific time. |
|
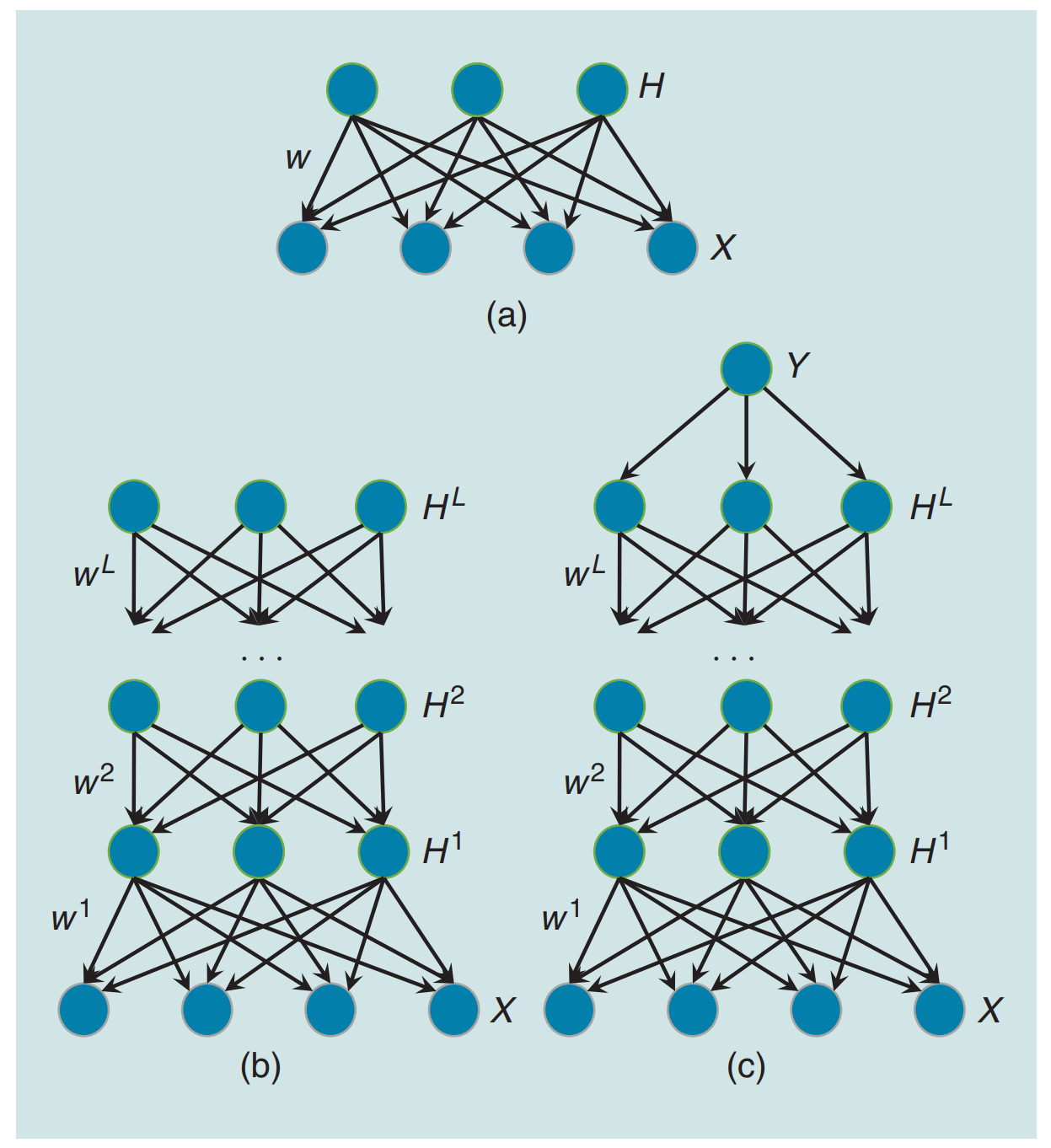
Siqi Nie, Meng Zheng, Qiang Ji IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018 A review of different structures of deep directed generative models and the learning and inference algorithms associated with the structures. We focus on a specific structure that consists of layers of Bayesian networks (BNs) due to the property of capturing inherent and rich dependencies among latent variables. |
|
|
|
IEEE Signal Processing Letters
International Journal of Computer Vision IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology IEEE Access European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) |
|
|
|
Interesting and exciting media post about my advisor and collaborators!
|
|
Thanks to Jon Barron for sharing source code for creating this page. |